Figure 4. Combined anti-viral effects of PF-429242 and Rib.
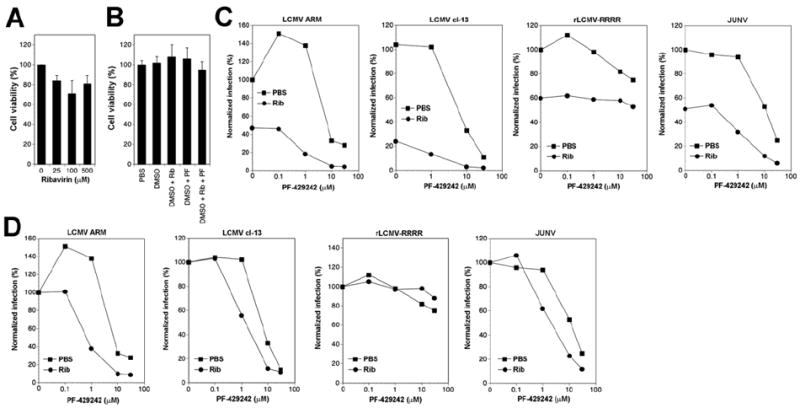
(A, B) Cytotoxicity of the combination of Rib and PF-429242 in A549 cells. Monolayers of A549 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of Rib and PF-429242 (PF). After 48 hours, cell viability was assessed using CellTiter-Glo® cell viability assay as in Fig. 2C. Values were normalized against the controls (DMSO vehicle) (means ± SD; n = 3). (C) Treatment of infected cells with Rib and PF-429242. A549 cells were infected with the indicated viruses at MOI = 0.01. After removal of unbound virus, fresh medium was added containing the indicated concentrations of PF-429242 either alone (PBS) or in combination with 25 μM Rib (Rib). After 48 hours, cells were detached, single cell suspensions prepared, and viral NP detected by intracellular staining as in 2E. Infection was normalized setting the percentage of infection in untreated cells (PBS, PF-429242 = 0) as 100%. Each point represents the average of two independent experiments. (D) Data shown in (C) with normalization for each series: the percentage of infection in cells not treated with PF-429242 (0) of each series (Rib, PBS) was set to 100%. A simple additive effect of PF-429242 and Rib on virus infection would result in overlapping curves as e.g. seen in case of rLCMV-RRRR that is not affected by PF-429242.
