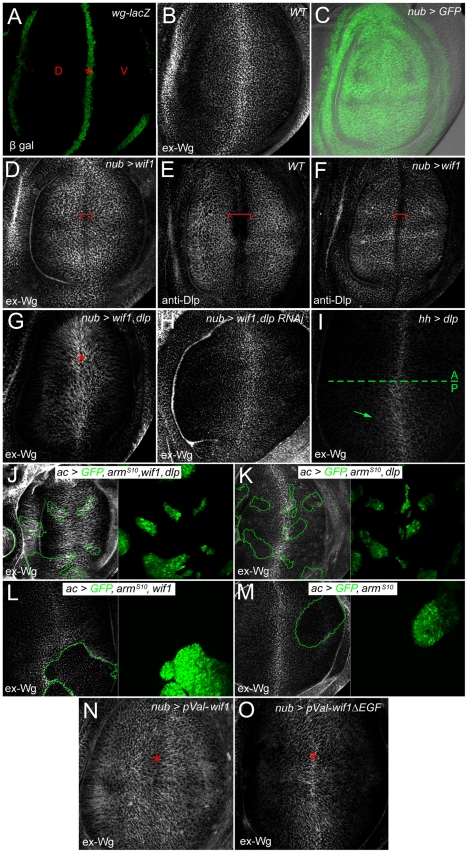
Figure 2. Wif1 stabilizes Wg on Dlp-expressing cells in late third instar wing discs.
Wing pouch regions of wing imaginal discs. (A) wg-lacZ expression along the prospective wing margin (asterisk) where prospective dorsal (D) and ventral (V) wing blade surfaces abut. (B) Extracellular Wg (ex-Wg) from the wg-expressing cells, which is high distally and lower proximally. (C) Pattern of nub-Gal4 expression, marked by UAS-GFP. In all subsequent panels, except for I-M, nub-Gal4 is used to drive UAS-transgene expression. (D) ex-Wg after expression of UAS-wif1. ex-Wg is higher on proximal cells than on distal ones (red bracket). (E) Anti-Dlp staining in wild-type wing disc. Dlp expression is downregulated in distal cells of the prospective wing margin (red bracket). (F) Anti-Dlp staining after UAS-wif1 expression. The width of the prospective wing margin region with reduced staining (red bracket) is narrowed compared to anti-Dlp staining in the wild-type disc in E. (G) ex-Wg staining after co-expression of UAS-wif1 and UAS-dlp. ex-Wg is increased at the wing margin (asterisk). (H) ex-Wg staining after co-expression of UAS-wif1 and UAS-dlp RNAi is similar to that in the wild-type disc in E. (I) Posterior expression of UAS-dlp (using hh-Gal4). ex-Wg accumulates in the posterior compartment. (J-M) Flpout actin-Gal4 (ac) clones marked with UAS-GFP (green). (J) High ex-Wg levels inside and, to a lesser extent, outside clones expressing: UAS-armS10, UAS-wif1, and UAS-dlp. (K) Low, largely unchanged ex-Wg levels inside clones expressing UAS-armS10 and UAS-dlp. (L) Reduced ex-Wg levels in clones expressing UAS-wif1 and UAS-armS10. zWIF1 increases ex-Wg outside the clone. (M) Reduced ex-Wg levels in clones expressing ArmS10. (N) After expression of pVal-UAS-wif1, ex-Wg staining is high proximally and low along the wing margin (asterisk). (O) Expression of pVal-UAS-wif1ΔEGF does not lead to a strong increase in proximal ex-Wg, and does not decrease ex-Wg along the wing margin (asterisk).