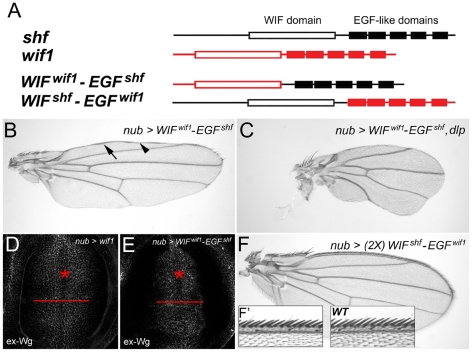
Figure 5. The EGF-like domains are interchangeable between Wif1 and Shf during Wif1-dependent Wg inhibition.
(A) Domain compositions of Wif1, Shf and the two chimeric constructs. Open boxes show the ‘WIF’ domain, filled boxes the EGF-like domains. (B–F) nub-Gal4-driven misexpression of respective transgenes. (B) UAS-WIFwif1-EGFshf strongly reduces the density of anterior wing margin bristles and interrupts L1. Arrow and arrowheads denote L1 or lack of thereof, respectively. (C) Co-expression of UAS-WIFwif1-EGFshf and UAS-dlp almost completely eliminates wing margin bristles and L1, and reduces the size of the wing. (D, E) Expression of either UAS-wif1 or UAS-WIFwif1-EGFshf similarly reduces ex-Wg levels on the surface of prospective margin cells (asterisks) and increases levels proximally. However, compared to UAS-wif1, UAS-WIFwif1-EGFshf expression does not increase ex-Wg as far proximally (compare red bars). (F, F′) Expression of two copies of UAS-WIFshf-EGFwif1 does not alter wing shape or size, and has no measurable effect on margin bristles (anterior margin details in F′).