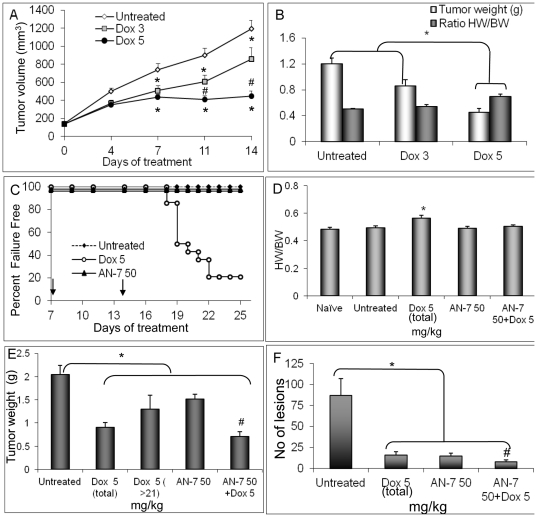
Figure 1. Effect of Dox, AN-7, and AN-7+Dox in the 4T1 murine mammary carcinoma model.
(A) In the preliminary experiment, female Balb/c mice carrying 75–180 mm3 subcutaneous 4T1 tumors were randomly divided into three groups (10 mice/group) and were injected ip once a week with either vehicle, 3 or 5 mg/kg Dox. Tumor volume was measured twice a week up to day 14 when the experiment was terminated (after 2 Dox treatments). Mean±SE of tumor volume was: *p<0.05, untreated vs. the other groups; #p<0.05, Dox 5 mg/kg vs. Dox 3 mg/kg. (B) Mean±SE of tumor weight and the ratio of heart-weight to body-weight (HW/BW, g/g), measured at the experiment termination point were: *p<0.01, Dox 5 mg/kg vs. all other groups. (C) In the pivotal experiment, the Percent Failure Free mice bearing 75–180 mm3 subcutaneous 4T1 tumors, was assessed by a Kaplan-Mier graph. The mice were assigned to the following treatments: saline vehicle ip (n = 7) or po (n = 7); ip Dox, 5 mg/kg once/week (n = 14); po AN-7, 50 mg/kg 3 times/week (n = 14); po AN-7+ip Dox (n = 14). The arrows on the x-axis indicate the point in time of the second and the third Dox treatment. (D) Mean±SE of heart-weight to body-weight ratios (HW/BW, g/g) at the above experiment end-point was #p<0.01, Dox 5 mg/kg vs. all other groups. (E) Tumor weight at the termination point (mean±SE) was: Dox 5 (total) represents the tumor weight of all the mice treated with 5 mg/kg Dox (n = 14), as measured at their individual end-points; Dox 5 (>21) represents the tumor weight of the mice (n = 5) treated with 5 mg/kg Dox and survived beyond day 21 of treatment. *p<0.02 all groups vs. untreated control; #p<0.05 AN-7+Dox vs. AN-7 or Dox 5 (total) or p<0.01 Dox 5 (>21). (F) Mean±SE of lung lesions for the various treatment groups is shown. *p<0.02, untreated vs. all treatment groups; #p<0.05, AN-7+Dox vs. AN-7 or vs. Dox.