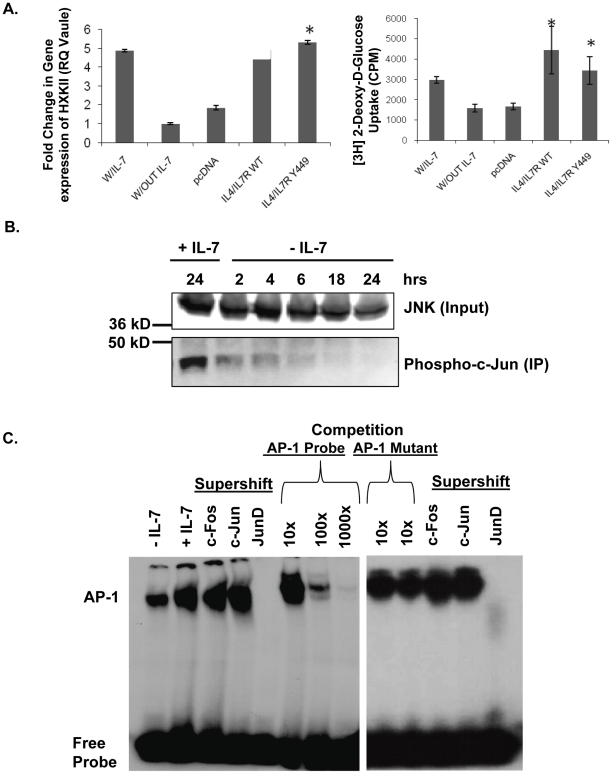
Figure 1. IL-7 signaling induces JNK activity and promotes JunD-containing AP-1 complexes.
(A) (Left panel) Quantitative PCR evaluation of HXKII gene expression in the IL-7 dependent T-cell line, D1, after culture with or without IL-7. D1 cells were also nucleofected with a chimeric IL-4/IL-7 receptor (IL-4/IL-7R WT), a chimeric IL-4/IL-7 receptor with a mutation in Y449 (IL4/IL7R Y449) or an empty vector (pcDNA), and stimulated with IL-4, as described in Methods. (Right panel) In cells treated as described above, glucose uptake was assessed by measuring the accumulation of radiolabeled 2-DOG as stated in Methods. (*) indicates a P value of <0.05. (B) To assess JNK kinase activity in response to IL-7, a kinase assay was performed. JNK was immunoprecipitated from whole cell lysates prepared from D1 cells cultured in the presence or absence of IL-7 for the times indicated and the capacity to phosphorylate the kit-supplied substrate, c-Jun, measured as indicator of kinase activity. As input control, pre-immunoprecipitation levels of JNK in lysates are shown. (C) Nuclear lysates prepared from D1 cells grown with or without IL-7 for 18 hours were assayed for AP-1 complex binding to DNA by EMSA, using a radiolabeled DNA probe containing the AP-1 consensus binding site. Supershifts were performed with antibodies specific for c-Fos, c-Jun or Jun-D. Competition was also performed using 10×, 100× or 1000× excess unlabeled AP-1 probe or AP-1 mutant probe. Results (A, B, and C) are representative of three or more independent experiments (values in graphs are mean ± SD).