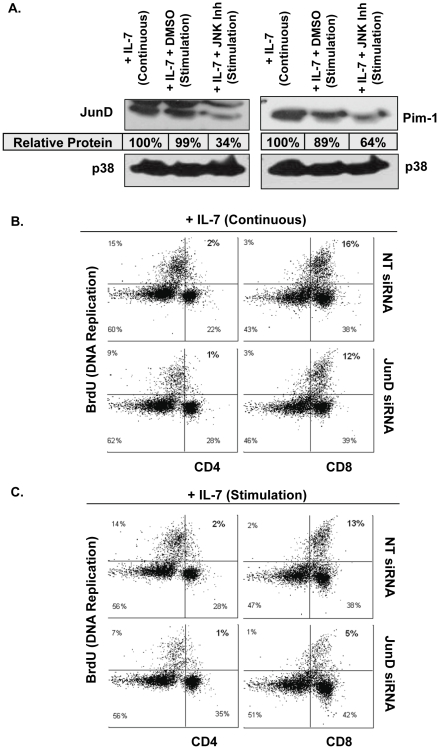
Figure 8. Inhibition of JunD Prevents IL-7 Induced Proliferation of Primary Lymphocytes.
(A) Lymph node T-cells were isolated from WT C57Bl/6 mice, cultured continuously with 150 ng/ml of IL-7 for 7 days (Continuous) or for 5 days, then deprived from IL-7 overnight, and IL-7 re-added for 24 hours (Stimulation) and treated with vehicle (DMSO) or 20 µM JNK inhibitor as described in Methods. Whole cell lysates were prepared from T-cells, subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted for Pim-1, JunD, and p38 MAPK as loading control. Tables indicate amounts of protein normalized to p38 MAPK content and shown relative to the IL-7 (Continuous) sample. Results are representative of two experiments performed. (B, C) Proliferation was measured by BrdU incorporation. Lymph node T cells were isolated from WT C57Bl/6 mice as described in (A) and treated with non-targeting control (NT) or JunD siRNA as described in Methods. Cells were assessed for BrdU incorporation and surface expression of CD4 and CD8 as determined by flow cytometric analysis of BrdU-PE and CD4- or CD8-PerCp fluorescence. Dot blots show percentages representing the population of cells that are non-proliferating (BrdU negative), proliferating (BrdU positive), and CD4+ or CD8+ as indicated by the quadrants. Quadrants were established using controls. Gating was performed to remove autofluorescent cells. Results are representative of duplicate samples.