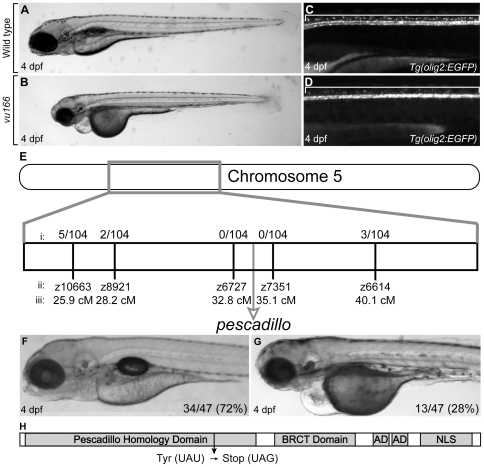
Figure 1. Characterization and genetic mapping of the vu166 mutant allele.
Lateral views of 4 dpf wild-type (A,C) and vu166−/− larvae (B,D). EGFP expression revealed oligodendrocytes in dorsal spinal cord of wild-type Tg(olig2:EGFP) larva (C, bracket). Fewer dorsal EGFP+ cells were evident in a vu166−/− larva (D). Bulked segregant analysis revealed that the vu166 allele links to chromosome 5 (E). The recombination frequencies (i) at various microsatellite markers (ii) at known locations (iii) along chromosome 5 show that the mutation lies near the pescadillo (pes) gene locus. The vu166 allele failed to complement the previously characterized peshi2 mutant allele, producing phenotypically wild-type (F) and mutant (G) larvae in a 3∶1 ratio. The Pes gene product (H) contains a highly conserved Pescadillo Homology domain, a BRCA1 C-terminal domain, two Acidic Domains (AD), and a Nuclear Localization Sequence (NLS). Sequencing of pes cDNA obtained from vu166 mutants revealed a single base pair mutation that creates a premature stop codon predicted to prematurely truncate the protein.