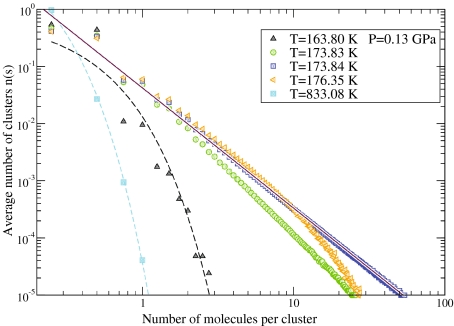
Fig. 2.
Distribution n(s) of clusters with finite size s formed by correlated hydrogen bonds in a non-crystallizing water monolayer. Calculations are for P = 0.13 GPa ≃ PC′, the liquid-liquid critical pressure, and different values of temperature for a system with N = 4×104 water molecules. For T = 173.84 K ≃ TC′, the liquid-liquid critical temperature, calculations (blue square points) decays as a power law n(s)~s − τ (continuous line). We find τ = 2.1±0.1, as expected from theory near a critical point [91]. Consistent with the theory, we find that n(s) cannot be described by a power law decay away from the critical point. This is the case, for example, at T = 173.83 K (green circles) and T = 176.35 K (orange triangles). We find that at temperatures far from the critical temperature, n(s) has an exponential decay. For example, we find an exponential decay (dashed lines) at T = 833.08 K (light blue square) and T = 163.80 K (black triangles)