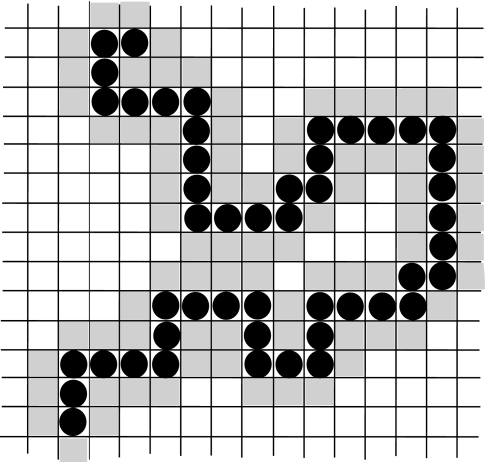
Fig. 4.
Example of configuration of a homopolymer in the coarse-grained model of a protein suspended in water. Each cell is occupied either by a water molecule (white and gray cells) or a hydrophobic homopolymer monomer (cells with a filled black circle). The gray cells represent the sites occupied by shell water. The enthalpy gain for HB formation between shell water molecules is larger than that between bulk water molecules, according to (22). Shell water molecules cannot form hydrogen bonds with nearest neighbor hydrophobic monomers