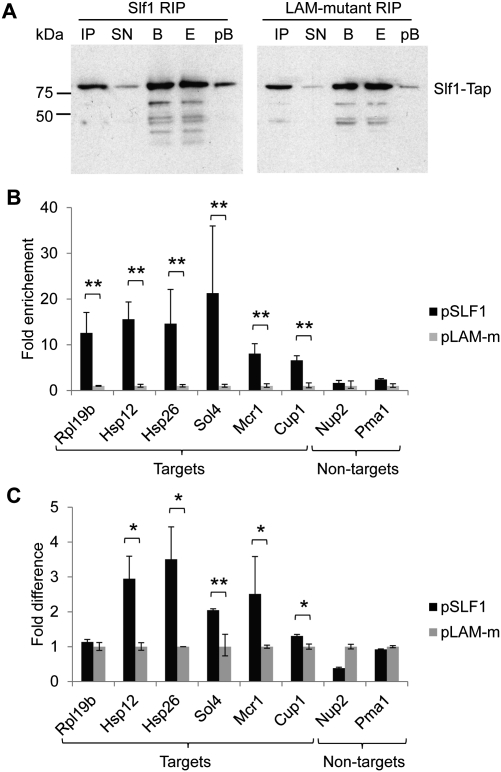
FIGURE 4.
Association of mRNAs with Slf1p depends on a functional LAM. (A) Immunoblot analysis following RIPs with TAP-tagged Slf1 (left) and the Slf1 LAM-mutant (right) expressed in slf1Δ cells using the peroxidase-anti-peroxidase soluble complex (PAP; see Materials and Methods). Lanes are as follows: IP, input yeast extract; SN, supernatant after incubation of extracts with IgG beads; B, captured beads; E, eluate from the beads; and pB, beads after elution of proteins with SDS-EDTA. (B) Four independent RIPs were performed with WT (pSLF1) or LAM-mutant (pLAM-m) SLF1, and the indicated mRNAs were quantified in RIP eluates by real-time qRT-PCR with cycle threshold (Ct) values normalized to mitochondrial 21S rRNA. Depicted is the fold difference in the abundance between WT and LAM-mutant RIP eluates. P-values were calculated based on ΔCt-values (t-test). **P < 0.001. (C) Comparative analysis of mRNA levels in the extracts (=input) used for RIP affinity purifications by qRT-PCR (two biological replicates). Mitochondrial 21S rRNA was used for normalization and averaged data for LAM-m was set to 1 (y-axis). P-values were calculated based on ΔCt-values (t-test). *P < 0.01, **P < 0.001.