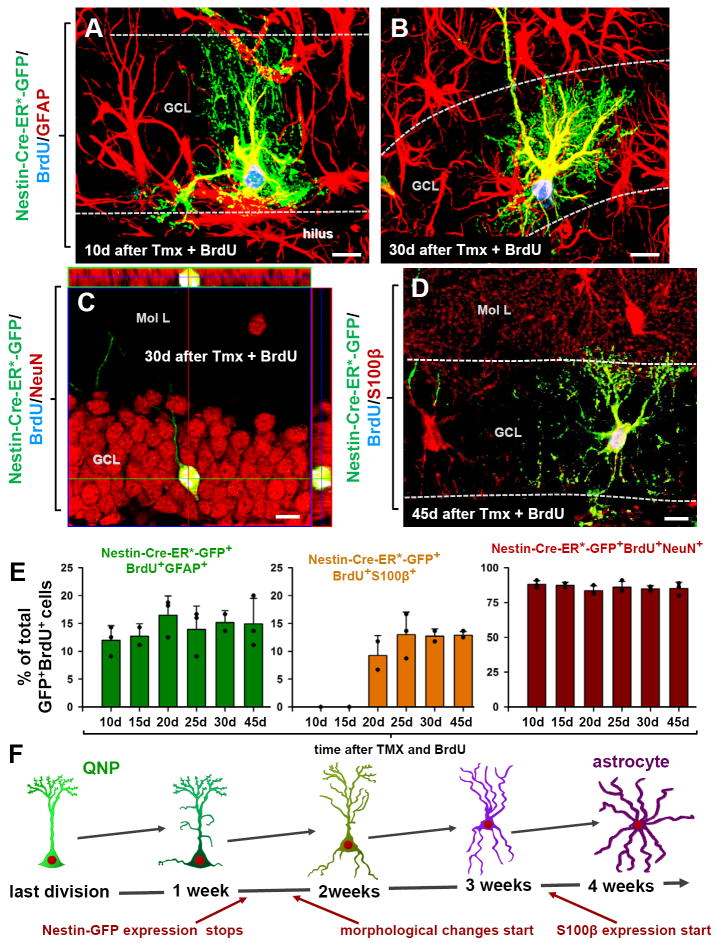
Fig. 5. QNPs undergo division-coupled astrocytic differentiation.
(A-D) Recombination in Nestin-CreER/Z/EG mice (3-4 months old) was induced by tamoxifen treatment. Dividing cells were labeled by BrdU. 10 days after tamoxifen induction and BrdU labeling, GFP+BrdU+ QNPs change their morphology, branching their apical radial processes and extending basal cytoplasmic extensions with multiple ramifications (A). 30 days later they extend processes from the soma, show characteristic star-shape morphology and extensive ramification of the branches and become indistinguishable from the surrounding stellar astrocytes (B). GFP+BrdU+NeuN+ granule neurons, detected 30 days after tamoxifen induction and BrdU injection; (C; shown with orthogonal projections). GFP+BrdU+S100β+ mature astrocytes, detected 45 days after tamoxifen induction and BrdU injection (D). Color channels are indicated. Bar is 10μm in A-D.
(E) Changes in GFP+BrdU+GFAP+ cells (labeled QNPs and new astrocytes together), GFP+BrdU+S100β+ cells (new mature astrocytes), and GFP+BrdU+NeuN+ cells (new neurons), as fraction of the total number of GFP+BrdU+ cells, after induction with tamoxifen and labeling with BrdU. Note that new mature astrocytes appear only 20 days after the induction and that the fraction of dividing QNPs and astrocytes does not undergo significant changes. Also note that the fractions of neurons and astrocytes among GFP+BrdU+ double-labeled cells is the same as for BrdU+ single-labeled cells in Fig.4.
(F) Schematic representation, with a temporal scale, of the changes that QNP undergoes when becoming an astrocyte, with gradual appearance of the apical, basal, and somatic processes.
See also Figures S5 and S6.