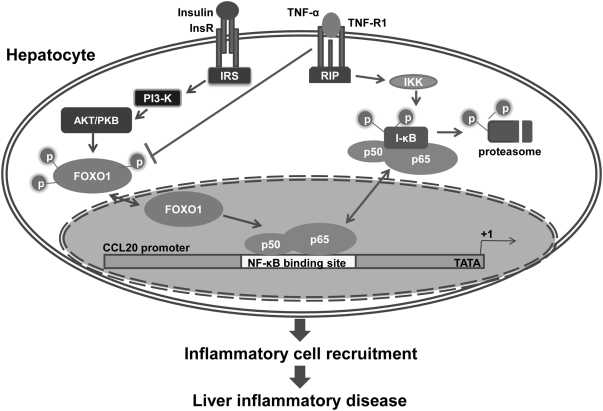
Fig. 9.
Proposed model for FOXO1-CCL20 pathway to enhance inflammatory infiltration in the insulin-resistant liver. Normally, insulin suppresses FOXO1 activation by sustaining FOXO1 phosphorylation through phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase/AKT pathway, preventing FOXO1 translocation to the nucleus. In the IR state, phosphorylated FOXO1 is reduced, and dephosphorylated FOXO1 is translocated into the nucleus to regulate transcription of its target genes. CCL20 may not be the direct target of FOXO1 because no FOXO1-binding sites are found in the proximal promoter of CCL20, and FOXO1 increases CCL20 promoter activity and expression only when the NF-κB pathway is activated by TNF-α. FOXO1 may somehow function as a coactivator of NF-κB to stimulate CCL20 production in hepatocytes, thereby exacerbating inflammatory infiltration in insulin-resistant livers. IRS, Insulin receptor substrate; insR, insulin receptor; RIP, receptor-interacting protein.