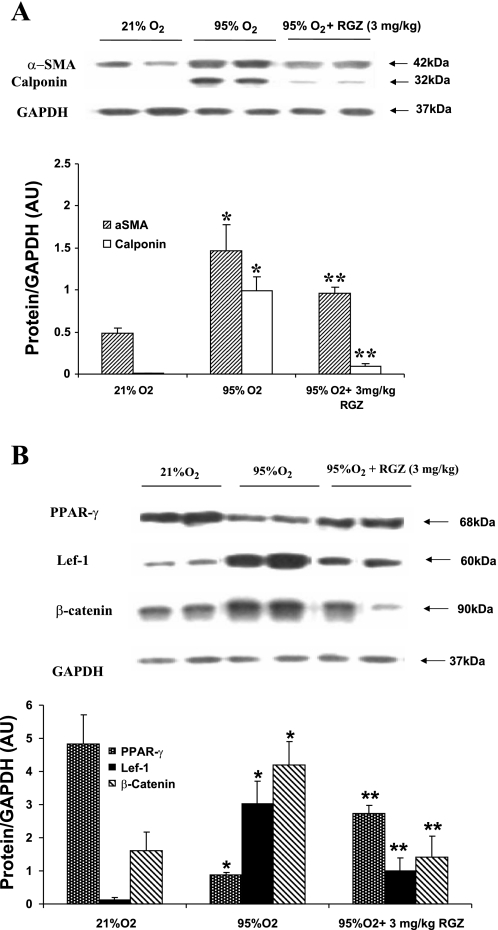
Fig. 2.
A: concomitant administration of 3 mg/kg RGZ inhibited hyperoxia (95% O2 for 7 days)-induced changes in α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and calponin expression. α-SMA and calponin were upregulated in hyperoxia, and RGZ administration inhibited the hyperoxia-induced upregulation of these proteins. Representative protein bands in duplicate and densitometric histogram of each group are shown (*P < 0.05, 95 vs. 21% O2, and **P < 0.05, 95% O2 + 3 mg/kg RGZ vs. 95% O2 only; n = 8). B: concomitant administration of 3 mg/kg RGZ inhibited hyperoxia (95% O2 for 7 days)-induced changes in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ), lymphoid enhancer factor 1 (Lef-1), and β-catenin in whole lung protein extract of 7-day-old rat pups. Seven-day hyperoxia exposure resulted in a significant decrease in PPARγ and a significant increase in Lef-1 and β-catenin protein expression, and concomitant RGZ administration prevented all of these changes. Representative protein bands in duplicate and densitometric histogram of each group are shown (*P < 0.05, 95 vs. 21% O2, and **P < 0.05, 95% O2 + 3 mg/kg RGZ vs. 95% O2 only; n = 8). AU, arbitrary units.