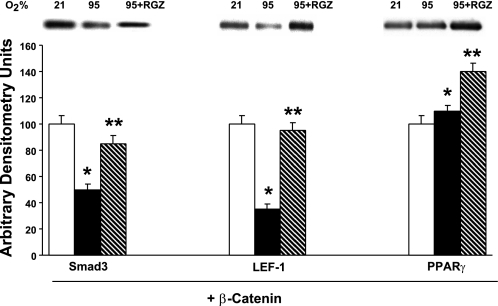
Fig. 7.
Evidence for interactions between the TGF-β, Wnt, and PPARγ signaling pathways in alveolar interstitial fibroblasts in response to hyperoxia. Immunoprecipitation of whole cell lysates of alveolar interstitial fibroblasts following 24-h exposure to either normoxia or hyperoxia (95% O2), with or without RGZ (10 μM) with anti-β-catenin antibody, and subjecting these complexes to Western blot analysis using anti-Smad3, anti-Lef-1, and anti-PPARγ antibodies showed that hyperoxia resulted in significant decreases in β-catenin-bound Smad3 and Lef-1, whereas levels of β-catenin-bound PPARγ increased. Treatment with RGZ both before and during hyperoxia exposure resulted in attenuation against hyperoxia-induced decreases in Smad3 and Lef-1 bound to β-catenin, whereas the level of β-catenin-bound PPARγ increased further (*P < 0.05, 95 vs. 21% O2, and **P < 0.05, 95% O2 + RGZ vs. 95% O2 only; n = 4).