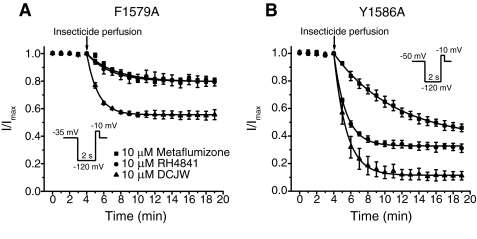
Fig. 6.
Effects of the F1579A and Y1586A mutations on the inhibition of Nav1.4 sodium channels by SCI insecticides. A, time course of sodium current inhibition in oocytes expressing Nav1.4/F1579A channels by metaflumizone, RH-4841, and DCJW. Oocytes were held at a holding potential of −35 mV and stimulated once every minute with a test pulse (20 ms) to −10 mV that was preceded by a 2-s hyperpolarization to −120 mV. After 4 min of stable control recordings at −35 mV, insecticides were perfused into the bath for 15 min; peak sodium currents were normalized to the mean sodium current amplitude obtained during the 4 min of stable control recordings before insecticide perfusion. Data were fitted using a first-order exponential decay function that yielded a single time constant (τ1); values are means ± S.E. of four to five individual experiments in separate oocytes. B, time course of sodium current inhibition in oocytes expressing Nav1.4/Y1586A channels by metaflumizone, RH-4841, and DCJW. Oocytes were held at a holding potential of −50 mV and stimulated once every minute with a 20-ms test pulse to 0 mV that was preceded by a 2-s hyperpolarization to −120 mV. After 4 min of stable control recordings at −50 mV, insecticides were perfused into the bath for 15 min; peak sodium currents were normalized to the mean sodium current amplitude during the 4 min of stable control recordings before insecticide perfusion. Data were fitted using a first-order exponential decay function that yielded a single time constant (τ1); values are means ± S.E. of three or more individual experiments in separate oocytes.