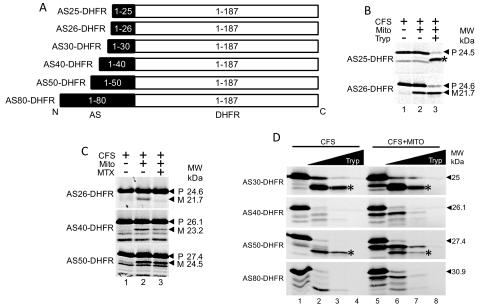
Fig. 5.
N-terminal 26 amino acids of AS target cargo protein DHFR to the mitochondria. A, the diagram shows the different AS-DHFR fusion constructs, where the full-length DHFR was fused to the varying length of N-terminal AS, as indicated. The black indicates AS, whereas the empty white boxes indicate DHFR. B, translocation of AS-DHFR fusions into mitochondria. Lane 1, CFS only. Lane 2, CFS incubated with mitochondria. AS25-DHFR is not cleaved when incubated with mitochondria, whereas AS26-DHFR is cleaved. Lane 3, mature AS26-DHFR is protected from protease, whereas precursor AS25-DHFR is digested. A fragment of AS25-DHFR is protected from proteolysis; however, this fragment is a proteolytic breakdown product that forms in the absence of mitochondria, indicated by a star. C, halting of translocation of AS-DHFR fusions by methotrexate indicates that between 41 and 50 amino acids are required to span the OMM and IMM, allowing cleavage of the AS-targeting sequence by MPP. Lane 1, CFS only. Lane 2, CFS incubated with mitochondria. All three constructs are cleaved to mature forms. Lane 3, addition of methotrexate (MTX) prevents cleavage of AS26-DHFR and AS40-DHFR, whereas AS50-DHFR is cleaved. D, comparison of protease digestion of AS30-DHFR, AS40-DHFR, AS50-DHFR, and AS60-DHFR shows changes in folding of the proteins. Lane 1, CFS only. Lanes 2 to 4, increasing concentrations of protease incubated with CFS. Lane 5, CFS incubated with mitochondria, with cleavage of each fusion protein. Lanes 6 to 8, increasing concentrations of protease incubated with CFS and mitochondria. Protected fragments from AS30-DHFR and AS50-DHFR form with CFS only and CFS with mitochondria (indicated by star). Occurrence of these bands depends on the size of the N-terminal AS sequence fused to DHFR.