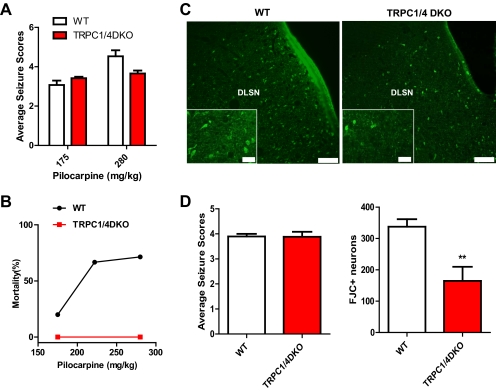
Fig. 4.
Seizure-induced neuronal cell death in the dorsolateral septum is significantly reduced in TRPC1/4 double-knockout mice. A, pilocarpine induces comparable intensities of seizures in wild-type and TRPC1/4 double-knockout (DKO) mice (p > 0.05, two-way analysis of variance). Pooled data (mean ± S.E.M.) were plotted (n = 24, 16 for WT at 175 and 280 mg/kg pilocarpine; n = 12, 6 for TRPC1/4 DKO at 175 and 280 mg/kg pilocarpine). See Materials and Methods for description of seizure scale. B, the mortality after pilocarpine injections within the first 24 h is significantly reduced in TRPC1/4 DKO mice (n = 12, 6) compared with wild-type mice (n = 24, 10, 16). C, representative images of FJC stained neurons in the dorsolateral septal nucleus (DLSN) of wild-type and TRPC1/4 DKO mice (2-day survival: wild-type, 175 mg/kg; TRPC1/4 DKO, 280 mg/kg). Scale bar, 0.20 mm (0.05 mm for insets). D, serial coronal sections containing septum (50 μm) were stained with FJC. FJC-positive neurons in the DLSN (see C) were counted in three sections approximately 300 μm apart. Mice (five WT treated with 175 mg/kg pilocarpine; five TRPC1/4 DKO treated with 280 mg/kg pilocarpine) included in analysis showed comparable seizures. TRPC1/4 DKO mice exhibit a significant reduction in FJC-positive neurons in the DLSN (two-tailed unpaired t test; **, P < 0.01).