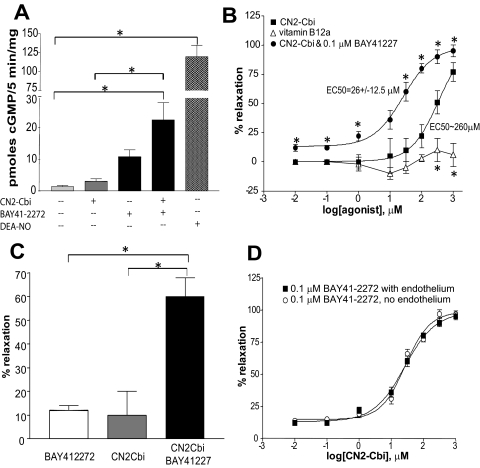
Fig. 6.
CN2-Cbi-dependent effect in intact cells and isolated aortic rings. A, levels of intracellular cGMP in MDA468 breast cancer cells after a 5-min exposure to the vehicle (0.1% DMSO), 100 μM CN2-Cbi, 2 μM BAY41-2272, a combination of 100 μM CN2-Cbi and 2 μM BAY41-2272, or 100 μM DEA-NO. B, concentration-dependent relaxation of phenylephrine-contracted rat aortic rings in response to vitamin B12 (▵) or CN2-Cbi alone (■) or in combination with 0.1 μM BAY41-2272 (▾). Data are means ± S.E.M. of four aortic rings obtained from two rats per each treatment. *, p < 0.05 versus CN2-Cbi. C, combined treatment with submaximal doses of BAY41-2272 (0.1 μM) and CN2-Cbi (30 μM CN2-Cbi) shows a synergistic effect in comparison to individual treatments with the same doses. *, p < 0.05. D, relaxation of endothelium-competent (■) and endothelium-denuded (○) precontracted aortic rings in response to various concentrations of CN2-Cbi in combination with 0.1 μM BAY41-2272. Data are means ± S.E.M. of three aortic rings obtained from three different rats.