Figure 6. A-type voltage-gated potassium channels and large conductance calcium-activated potassium (BK) channels are expressed in corticotrophs.
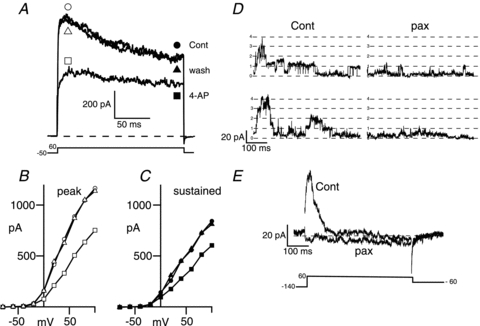
A, representative voltage-clamp recording of a metabolically intact corticotroph displaying significant inactivating outward current when depolarised from a holding potential of −50 mV to +60 mV before (cont, circles) during (4-AP, squares) and after washout (wash, triangles) with 4-aminopyridine (4-AP, 1 mm) an inhibitor of A-type potassium channels. B and C, current–voltage relationship for the cell in A determined at the peak outward current shown by the open symbols in A (B) or during the sustained phase (180–200 ms into pulse) shown by the filled symbols in A (C). D, single channel recordings from inside-out membrane patches exposed to 5 μm intracellular free calcium determined during a step pulse to +60 mV before (Cont) and after application of the specific BK channel inhibitor paxilline (pax, 1 μm). E, ensemble average traces in the presence and absence of paxilline from 15 recordings as in D.
