Figure 8. Spontaneous cardiac baroreflex sensitivity (cBRS) at rest, during handgrip exercise under free-flow conditions (open bars) and with graded partial flow restriction (filled bars).
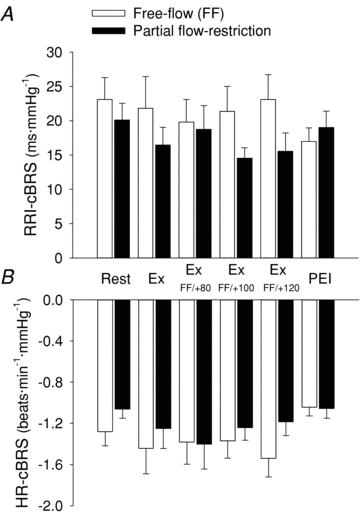
Spontaneous cBRS calculated using either R-R interval (RRI-cBRS, A) or heart rate (HR-cBRS, B). FF, free flow; PFR, partial flow restriction; RRI, R-R interval; Ex, rhythmic handgrip exercise at 35% of maximum voluntary contraction; Ex FF/+80, Ex FF/+100 and Ex FF/+120, handgrip exercise without or with upper arm cuff inflation to 80, 100 and 120 mmHg, respectively; PEI, post-exercise ischaemia. Statistical analysis using 2 × 6 repeated measures ANOVA indicated no significant main effects of phase (P = 0.486 and P = 0.246 for RRI-cBRS and HR-cBRS, respectively) and trial (P = 0.113 and P = 0.159 for RRI-cBRS and HR-cBRS, respectively) and no significant interactions (P = 0.183 and P = 0.664 for RRI-cBRS and HR-cBRS, respectively).
