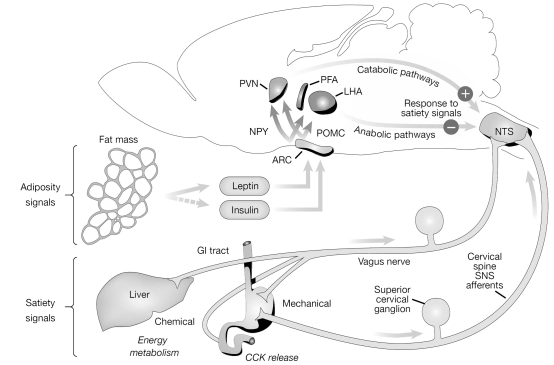
Fig. (1).
Neuroanatomical model summarizing the different pathways that control energy homeostasis. During meals, episodic and tonic signals, such as the satiety signals cholecystokinin (CCK) and the adiposity signals leptin and insulin, are conveyed through the vagus nerve to the arcuate nucleus (ARC) and nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS). These signals interact with neurons that synthesize anorexigenic and orexigenic neuropeptides, like proopiomelanocorticotropin (POMC)/cocaine amphetamine regulating transcript (CART) or neuropeptide Y (NPY)/agouti related peptide (AgRP), respectively, which in turn project to other hypothalamic areas including the paraventricular nuclei (PVN) and the lateral hypothalamic area (LHA). Figure reproduced, with permission, from Reference [5]. Abbreviations: GI, gastrointestinal; PFA, perifornical area; SNS, sympathetic nervous system.