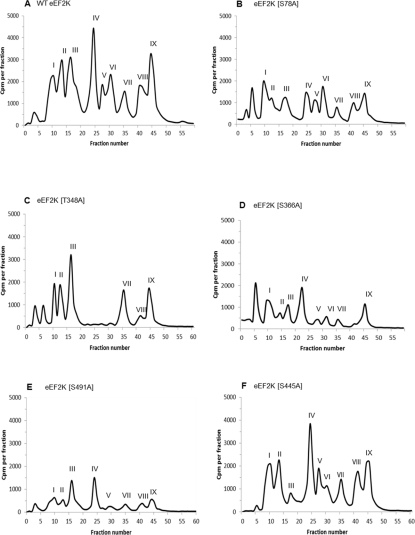
Figure 2. HPLC profiles of 32P-autophosphorylated wild-type and mutant eEF2K preparations following trypsin digestion.
Tryptic phosphopeptides from autophosphorylated eEF2K were separated by reverse-phase HPLC as described in the Experimental section. The major radiolabelled peaks are indicated by roman numerals. Phosphorylation sites detected in the peaks are summarized in Table 1 and discussed in the text. HPLC profiles are shown for wild-type (WT) eEF2K (A) and the eEF2K[S78A] (B), eEF2K[T348A] (C), eEF2K[S366A] (D), eEF2K[S491A] (E) and eEF2K[S445A] (F) mutants.