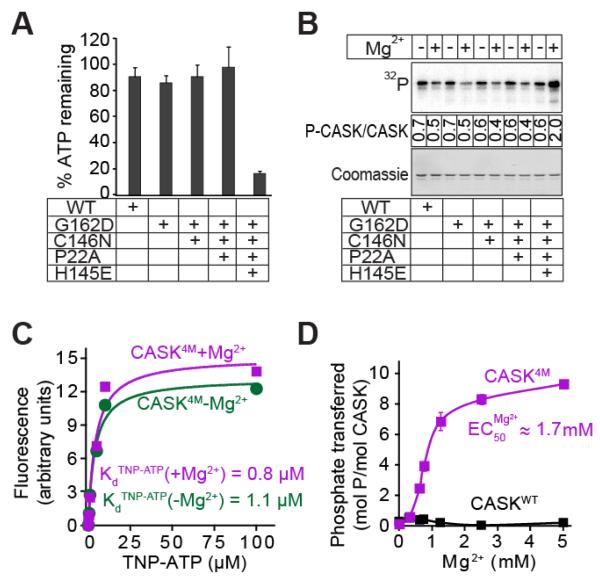
Figure 2. Effect of divalent ions on nucleotide-binding and hydrolysis.
A. ATP consumption by WT or mutant CASK CaM-kinase domain. In Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.0) supplemented with Ca2+ (1 mM), CaM (4 μM), and Mg2+ (2 mM), indicated variant of CASK CaM-kinase domain (1 μM), Autocamtide-2 (100 μM) and ATP (50 μM) were incubated for 60 min. The amount of ATP remaining was detected with KinaseGlotm. Data represents means ± standard deviation of three independent experiments.
B. Autophosphorylation of WT and mutant CASK CaM-kinase domains. The indicated variants of CASK CaM-kinase domain (1 μM) were incubated in Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.0) with Na+-γ32P-ATP (50 cpm/pmol; -Mg2+) or 10 mM Mg2+-ATP (+Mg2+) at 30°C with shaking for 2 h. The proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane, and visualized by phosphorimager scanning (upper panel). Ponceau staining was used for loading control (lower panel). Mean stoichiometry of phosphate incorporation (phosphates/CASK molecule) from three independent experiments are shown between the panels.
C. TNP-ATP binding. Increasing amounts of TNP-ATP were added to cuvettes containing 10 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.0, 1 μM CASK4M, and either 4 mM EDTA (magenta symbols) or 200 μM Mg2+ (green symbols). The TNP-ATP fluorescence of the samples (excitation: 410 nm; emission: 541 nm) is plotted after subtracting background TNP-ATP fluorescence obtained with parallel samples, which contained the same TNP-ATP, Tris-HCl, EDTA, or Mg2+ concentrations but lysozyme instead of CASK. The plot is a representative of three independent experiments.
D. Effect of Mg2+ on kinase activity of CASK4M. Indicated variants of CASK CaM-kinase domain (2 μM), autocamtide-2 (100 μM) and γ32P-ATP (250 μM; 250 cpm/pmol) in Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.0) were incubated for 10 min with increasing amounts of Mg2+. Amount of phospho-autocamtide-2 generated was estimated by scintillation counting of dot-blots on nitrocellulose membrane. Data shown are means ± standard errors of the means (SEMs; n=3).