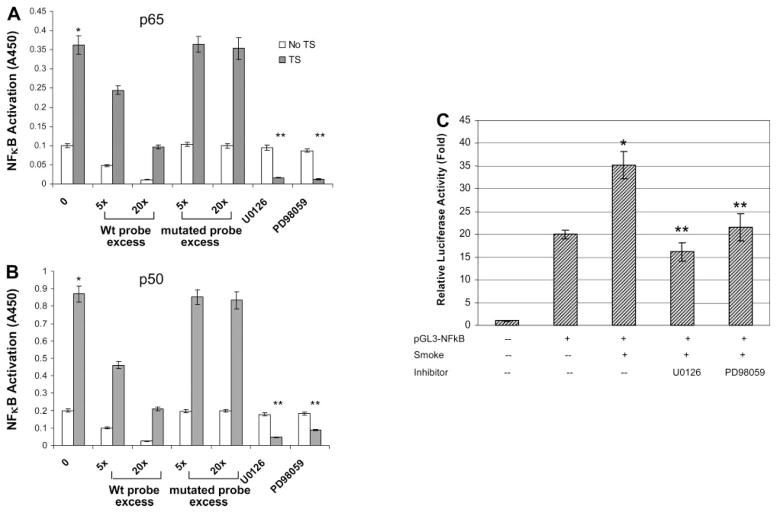
Fig. 8.
Decrease of TS-induced NF-κB binding and promoter activity by ERK 1/2 inhibitors. A and B: extracted nuclear proteins without or with TS exposure were added into 96-well plates that had prebound NF-κB duplex DNA. Microwells bearing the biotinylated NF-κB DNA probe (1 pmol) were incubated with an increasing excess of the nonbiotinylated probe, containing either the wild-type (wt) or the mutated NF-κB-binding consensus sequence. Specific DNA binding activity for either p65 (A) or p50 (B) was determined by measured activity after incubation with respective primary antibody against p65 or p50. C: A549 cells were transiently transfected with a NF-κB-containing plasmid linked to the pGL3 basic vector and then treated without or with ERK 1/2 inhibitors. After TS exposure, cell supernatants were collected and assayed for luciferase activity as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. Triplicate samples were harvested from each condition, and results are expressed as relative fold increase in luciferase activity compared with empty vector control. *P < 0.05, compared with non-smoke-treated basal activity; **P < 0.05, compared with TS-treated groups.