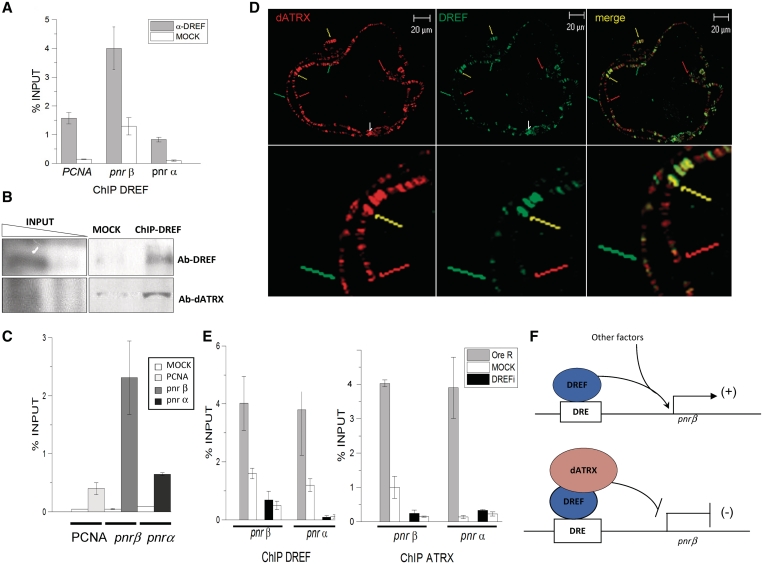
Figure 6.
A XNP/dATRX–DREF complex binds the DRE-pnrβ element. (A) DREF-ChIP assay from embryos overexpressing XNP/dATRX using an Act5C-Gal4 driver. Note that even when XNP/dATRX overexpression reduces pnr mRNA levels (Figure 2), DREF is still located at the pnr-β and pnr-α-DRE elements. The ChIP experiment was performed by triplicate (P = 0.001). (B) ChIP-western assay. ChIP was performed with the anti-DREF antibody and the precipitated chromatin analyzed in a typical western blot to search for the presence of DREF and dATRX. Note that both proteins can be detected. (C) Re-ChIP experiment using the DREF antibody for the first ChIP and then the XNP/dATRX antibody for the Re-ChIP. An unrelated antibody was used as negative control for the first ChIP and then immunoprecipitated with the dATRX antibody (white bars, MOCK). The Re-ChIP shows the average of three independent experiments (P = 0.01). (D) Polytene chromosomes prepared from wild-type larvae were simultaneously stained with the anti-DREF (green signal) and anti-XNP/dATRX antibodies (red signal). Several merge bands containing both factors can be visualized (yellow arrows), regions where only XNP/dATRX is present (red arrows) and regions where only DREF is present (green arrows). (E) ChIP experiments using the DREF and XNP/dATRX antibodies in wild-type and DREFi knocked-down embryos. The genotype of the organisms tested is Act5C-Gal4/+; UAS-DREFi/+. OreR corresponds to immunoprecipitated chromatin from wild-type organism (gray bars). DREFi corresponds to immunoprecipitated chromatin from embryos expressing the anti DREF RNAi (black bars). Mock is the incubation with unrelated antibody (white bars). Antibodies used for each IP are indicated at the bottom of the figure. (F) Model on the role of DREF and XNP/dATRX in the transcriptional regulation of pnr-β. Among other factors that regulate pnr gene expression during development, the interaction between DREF and dATRX may participate in the establishment of an active or negative effect in gene regulation.