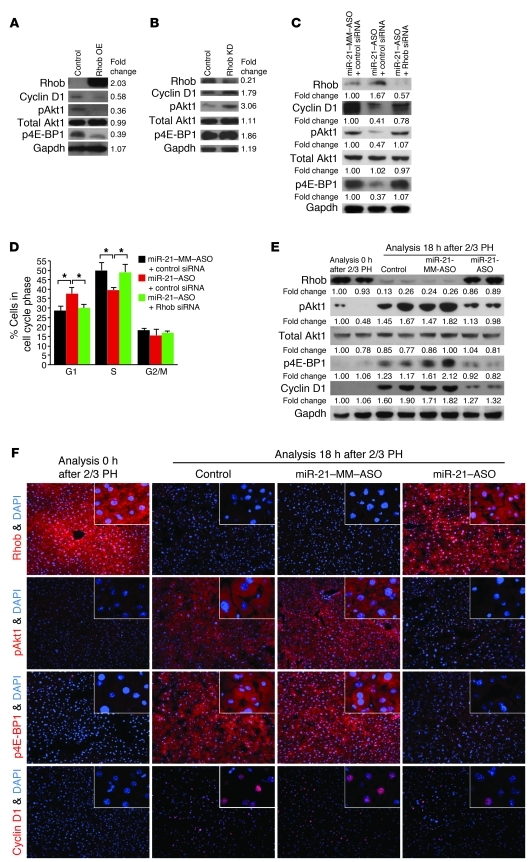
Figure 6. miR-21 promotes cyclin D1 translation in liver regeneration by relieving Akt1-mediated activation of mTORC1 from suppression by Rhob.
(A) Immunoblotting showed that Rhob overexpression (OE) plasmid transfection into Hepa1,6 cells decreased levels of cyclin D1, Akt1 activated by phosphorylation at Ser473 (pAkt1), and 4E-BP1 inhibited by phosphorylation at Thr37 and/or Thr46 (p4E-BP1). Cells transfected with empty overexpression plasmid were used as control. (B) Additional Rhob knockdown (KD) with a shRNA plasmid increased cyclin D1, pAkt1, and p4E-BP1 levels. (C) Immunoblotting showed that miR-21–ASO transfection into Hepa1,6 cells increased Rhob and decreased cyclin D1, pAkt1, and p4E-BP1 levels. Additional Rhob knockdown with siRNA restored cyclin D1, pAkt1, and p4E-BP1 levels. (D) Cell cycle phase distribution analysis by flow cytometry showed Rhob-dependent accumulation of miR-21–ASO–transfected cells in G1 phase. Cells transfected with miR-21–MM-ASO and negative control siRNA were used as control. Numbers indicate protein levels relative to control. Results are representative of 3 separate experiments (Supplemental Figure 12, A–C). (E) Immunoblotting showed failure to decrease Rhob and increase pAkt1, p4E-BP1, and cyclin D1 levels in the liver after 2/3 PH in mice injected with miR-21–ASO compared with mice injected with carrier (Control) or miR-21–MM–ASO. Liver samples were obtained by 2/3 PH and 18 hours later. Numbers indicate protein levels relative to time point 0 hours after 2/3 PH. (F) Confirmation of the immunoblotting results by immunostaining (red). Original magnification, ×200; ×400 (insets). At least 3 mice were analyzed for each time point and treatment (Supplemental Figure 12D). Carrier, miR-21–MM–ASO, or miR-21–ASO was injected at 6 hours after 2/3 PH. Gapdh was analyzed as a loading control. Data represent mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05.