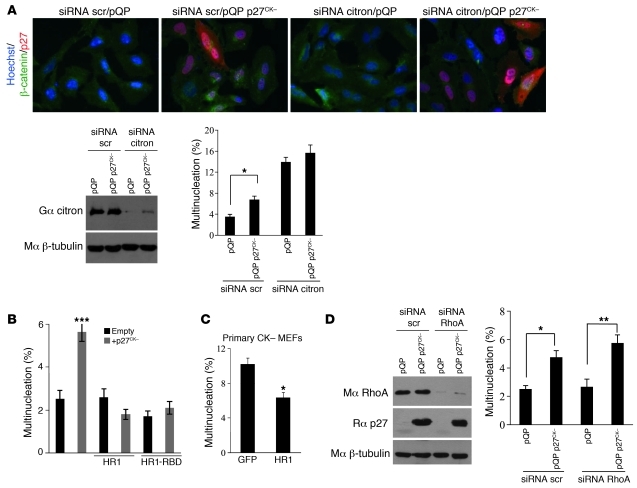
Figure 6. p27CK– interferes with citron-K function.
(A) p27CK– does not affect the multinucleation caused by citron-K depletion. HeLa cells were transfected with scrambled (scr) or citron-K siRNAs and plasmids expressing p27CK– or empty vector (pQP). Citron-K knockdown was controlled by immunoblotting with goat anti-citron antibodies; β-tubulin levels were used as loading control. Multinucleation was quantified in cells (500 cells/condition, n = 3) stained with β-catenin and p27 antibodies and Hoechst (original magnification, ×400). Results were analyzed using 1-way ANOVA with the Tukey-Kramer multiple comparison test; *P < 0.05. (B) The minimal p27-binding domain of citron-K (HR1) rescues the multinucleation caused by p27CK– overexpression. HeLa cells were transfected with p27CK– and/or different domains of citron-K. Multinucleation was quantified (500 cells/condition, n = 3). Results were analyzed by 1-way ANOVA with the Newman-Keuls test; ***P < 0.001. (C) The HR1 domain rescues the multinucleation in p27CK– primary MEFs. p27CK– primary MEFs were transfected with GFP or with the HR1 domain, and multinucleation was evaluated 48 hours later (350–600 cells/condition, n = 3). Results were analyzed using Student’s t test; *P < 0.05. (D) RhoA depletion has no effect on p27CK–-induced multinucleation. HeLa cells were transfected with scrambled or RhoA siRNA and plasmids expressing p27CK– or empty vector (pQP). RhoA knockdown and p27 expression were controlled by immunoblotting with anti-RhoA and anti-p27 antibodies; β-tubulin levels were used as loading control. Multinucleation was quantified (500 cells/condition, n = 3). Results were analyzed as in A; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (A–D) Error bars represent SEM.