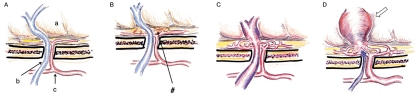
Figure 4.
Mechanism of development of the DAVF: an ethmoidal (anterior skull base) DAVF as a representative of the non-sinus type DAVF. A) Normal state. A, frontal cortex; b, frontal emissary vein; c, dural branches from anterior ethmoidal artery. B) Neovascularization and dilatation induced with dural inflammation (#). C) AV shunt formation at the level of dural arteriole and reflux into an EV (initial stage of DAVF). D) Shunt development and increased reflux into the varicose cortical vein (white arrow) following the occlusion of an emissary vein.