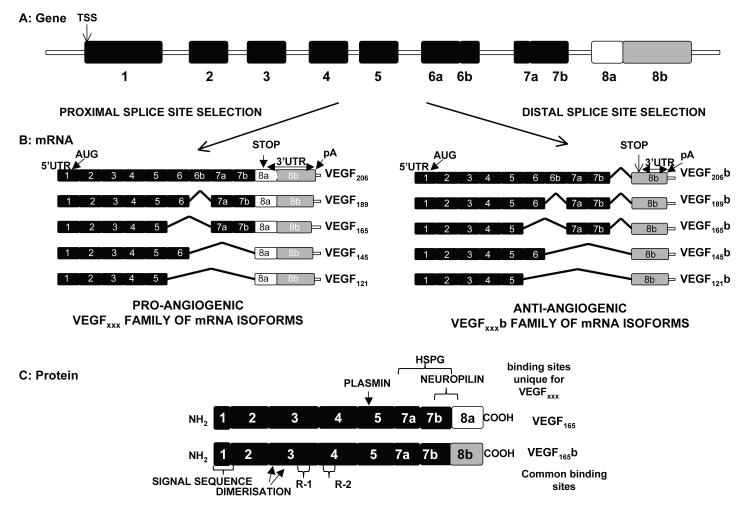
Figure 1. Organisation of the VEGF-A gene.
A. Gene structure. TSS=transcriptional start site. B. mRNA species. Alternative splicing of VEGF-A gene in the terminal exon results in two families of isoforms, the pro-angiogenic VEGFxxx, and the anti-angiogenic VEGFxxxb isoforms. AUG= start site for translation, UTR=untranslated region, pA = poly adenylation site. C. Protein structure of two major isoforms of each family. This C-terminal splicing leads to an alternative last six amino acids (CDKPRR or SLTRKD). The isoforms are termed according to the amino acid number of the resulting protein (xxx). HSPG=heparin sulphate proteoglycan, R1=VEGF receptor 1, R2 =VEGF Receptor 2 (not to scale).