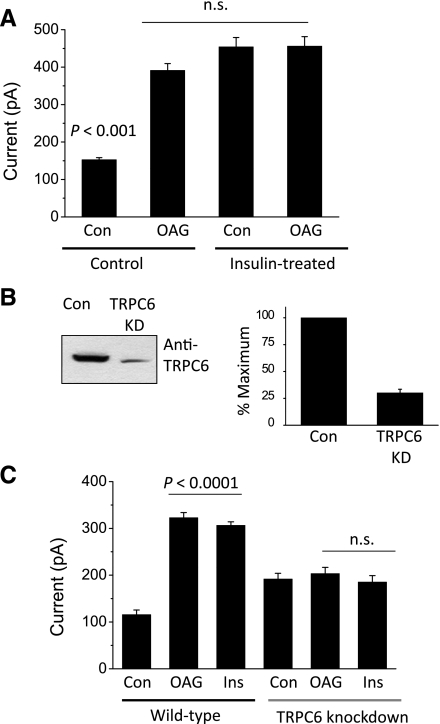
Fig. 4.
Insulin activates OAG-sensitive currents in podocytes that are eliminated by TRPC6 knockdown. A: insulin treatment occludes electrophysiological responses to OAG in podocytes. Control podocytes, or podocytes treated with 100 nM insulin for 12 h, were exposed to vehicle or 100 μM OAG for 5 min, and whole cell quantification of currents at +80 mV was carried out as in Figs. 2 and 3. Bars represent means ± SE for 10 cells in each group. Data were analyzed by 2-way ANOVA and Tukey's post hoc test. The effect of a combination of insulin and OAG was not significantly different from those evoked by either OAG or insulin alone. B: representative immunoblot analysis (left) and densitometric quantification of 3 repetitions of that experiment showing reduction in total TRPC6 expression in a cell line stably expressing an shRNA targeting TRPC6 compared (39) to a control cell line. C: mean currents at +80 mV recorded cells treated with vehicle, with 5 min of OAG, or 24 h of insulin in wild-type podocytes or in TRPC6 knockdown podocytes, as indicated. Data were analyzed by 2-way ANOVA, which showed that TRPC6 knockdown had a significant (P < 0.005) interaction effect on responses to OAG and insulin. Post hoc analysis indicated that responses to OAG and insulin were eliminated in TRPC6 knockdown cells.