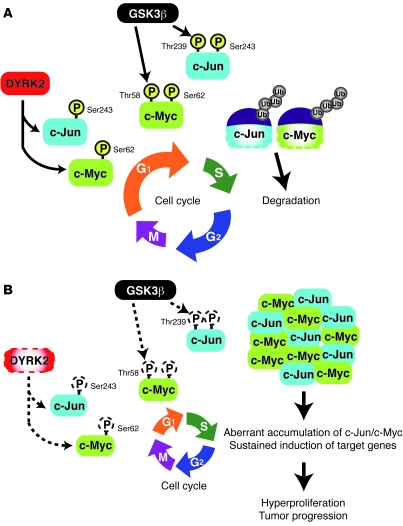
Figure 8. The model of DYRK2-mediated cell cycle regulation.
(A) At the late G1 phase, c-Myc and c-Jun are phosphorylated by DYRK2, which serves as a priming site for binding of GSK3β. GSK3β then obtains the license to phosphorylate (P) c-Jun and c-Myc via recognition of priming phosphorylation. Phosphorylated c-Jun and c-Myc bind to the ubiquitin ligase for their degradation. (B) In the absence of DYRK2, GSK3β is unable to phosphorylate c-Jun and c-Myc. Unphosphorylated c-Jun and c-Myc escape from the ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation. Accumulation of c-Jun and c-Myc induces their target genes, such as cyclin E.