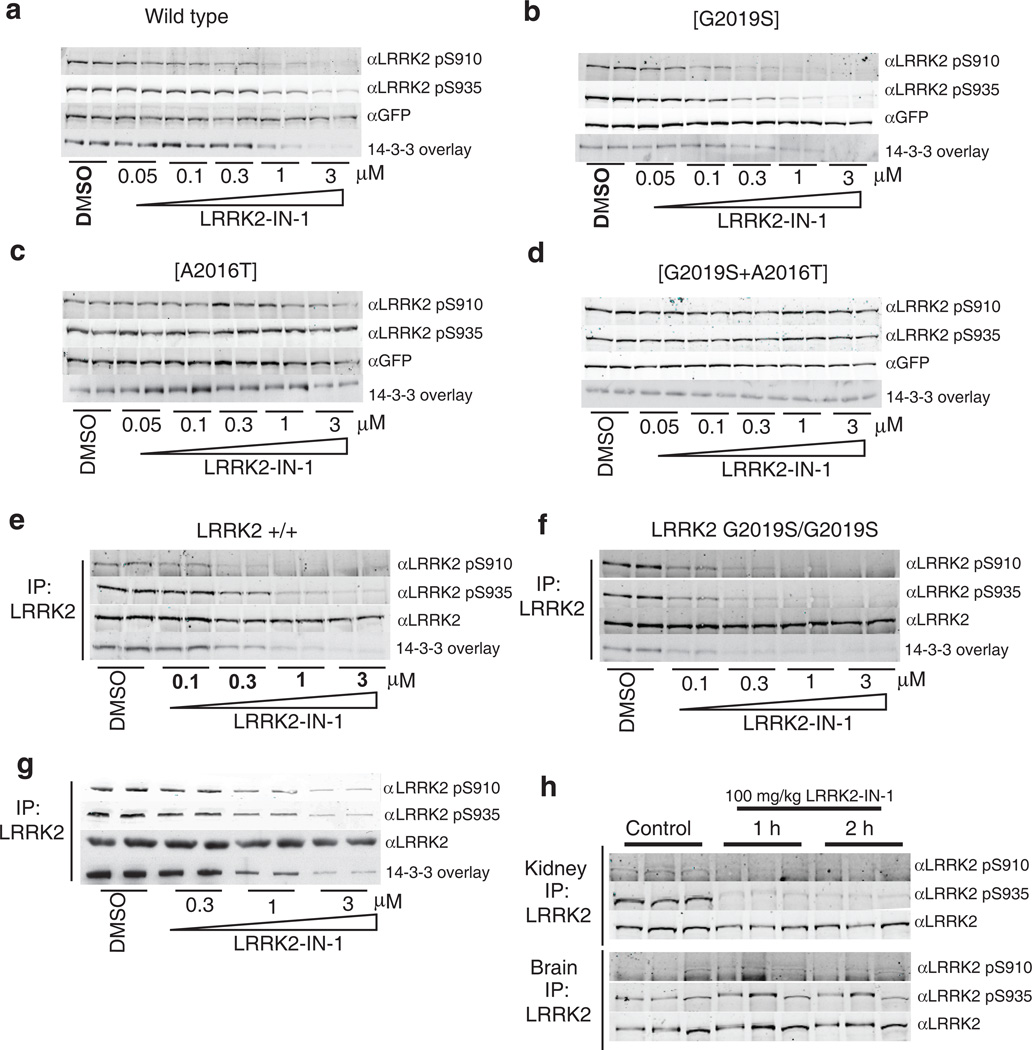
Figure 2. LRRK2-IN-1 inhibits LRRK2 in vivo.
(a) HEK 293 cells stably expressing wild type GFP-LRRK2 were treated with DMSO or increasing concentrations of LRRK2-IN-1 for 90 min. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting for detection of LRRK2 phosphorylated at S910 and S935 and for total GFP-LRRK2. 14-3-3 binding was measured by overlay assay following immunoprecipitation of LRRK2 with GFP-binder Sepharose. (b) As in (a) except HEK 293 cells stably expressing GFP-LRRK2 [G2019S] were utilized. (c) As in (a) except HEK 293 cells stably expressing drug resistant GFP-LRRK2 [A2016T] were utilized. (d) As in (a) except HEK 293 cells stably expressing drug resistant GFPLRRK2[ A2016T+G2019S] cells were utilized. (e) Endogenous LRRK2 was immunoprecipitated with anti-LRRK2 100-500 from EBV immortalized human lymphoblastoid cells from a control subject and a Parkinson’s disease patient homozygous for the LRRK2 [G2019S] mutation. (f) Following treatment of the cells with DMSO or the indicated concentrations of LRRK2-IN-1 for 90 min. Immunoprecipitates were subjected to immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibody as well as 14-3-3 overlay for western analysis. Immunoprecipitations were performed in duplicate and results are representative of at least two independent experiments. (g) As in (e) except that human SHSY5Y cells were utilized. (h) 100 mg/kg LRRK2-IN-1 was administered by intraperitoneal injection into wild type mice (n=3 per group). Tissues were collected and endogenous LRRK2 was immunoprecipitated and analysed for S910 and S935 phosphorylation as above. Quantitation of immunoblots along with original images are available in Supplementary Fig. 11