Figure 1.
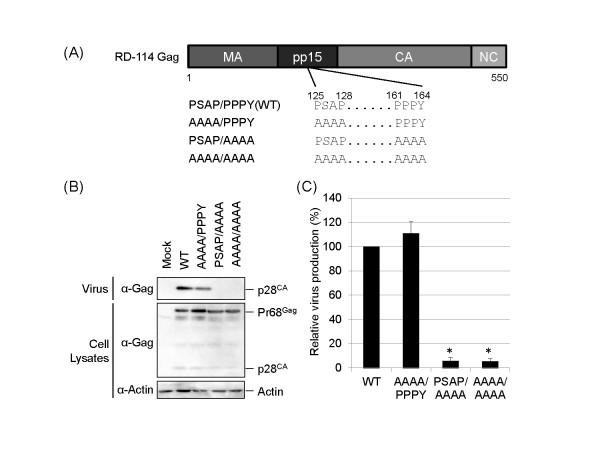
Identification of the L-domain, which is critical for RD-114 virus budding. (A) Schematic representation of RD-114 Gag and the L-domain mutants. The positions of the two putative L-domain motifs are indicated. (B and C) 293 T cells were transfected with the RD-114 infectious clone for wild-type (pTERD-114) or the L-domain mutant (0.5 μg). Cells and viruses were collected at 72 h after transfection, and analyzed by Western blotting (B) and real-time RT-PCR targeting the pol region (C). The virus production from cells expressing wild-type (WT) RD-114 was set to 100%. The data are shown as averages and standard deviations of 3 independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by using the Student's t-test (*: p < 0.01)
