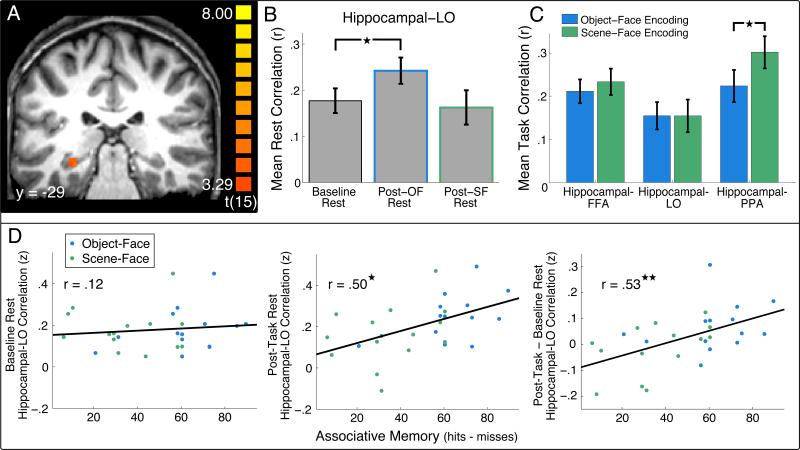
Figure 3. Hippocampal-cortical correlations during Rest and Encoding tasks.
(A) Hippocampal ROI identified from a subsequent associative memory contrast of associative hits > associative misses shown in coronal section on a high resolution anatomical image from an individual subject. Color indicates the value of the t-statistic from the contrast of associative hits – associative misses. (B) Mean BOLD correlation across subjects between the hippocampal ROI and LO during baseline and post-task rest periods. A significant increase in correlation was found from the Baseline Rest to the Post-OF Rest (★P < .05). All comparisons between correlation values were performed on Fisher Z-transformed correlation (r) values. (C) Mean correlations during Object-Face and Scene-Face Encoding tasks between the hippocampal ROI and the right FFA (left), LO (middle), and PPA (right). Significantly higher hippocampal-PPA correlations were found during Scene-Face compared to Object-Face Encoding (★P < .05). (D) Correlation between associative memory performance and hippocampal-LO BOLD resting correlations across individual subjects. During Baseline Rest, no significant correlation was seen between hippocampal-LO correlations and associative memory (left). For the post-task rest (Post-OF and Post-SF Rest), a significant correlation was found with associative memory for object-face and scene-face pairs (★P < .05, middle). The difference in hippocampal-LO correlations between post-task (Post-OF and Post-SF Rest) and Baseline Rest was also significantly correlated with associative memory (★★P < .005, right). All correlation values are Z-transformed correlation (r) values. Blue data points indicate Object-Face associative memory and Post-OF Rest correlations while green data points indicate Scene-Face memory and Post-SF Rest correlations.