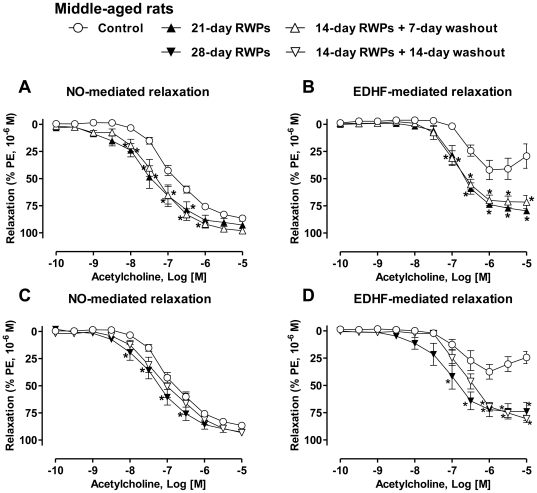
Figure 3. The RWPs-induced Improvement of endothelial dysfunction in the mesenteric artery persists after 7 and 14-day washout periods.
Middle-aged rats (46-week old) received RWPs (100 mg/kg/day) in the drinking water for either 21 days or 14 days followed by a 7-day washout period (a, b), and for 28 days or 14 days followed by a 14-day washout period (c, d). NO-mediated relaxations were determined in rings contracted with phenylephrine (1 µM) in the presence of indomethacin (10 µM) and charybdotoxin (CTX, 100 nM) plus apamin (APA, 100 nM) to inhibit the participation of prostanoids and EDHF, respectively (a, c). EDHF-mediated relaxations were recorded in the presence of indomethacin (10 µM) and Nω-nitro-L-arginine (L-NA, 300 µM) to rule out the participation of prostanoids and NO, respectively (b, d). Results are shown as means ± SEM of 5 to 6 rats. *P<0.05 indicates a significant difference versus the middle-aged rat control group.