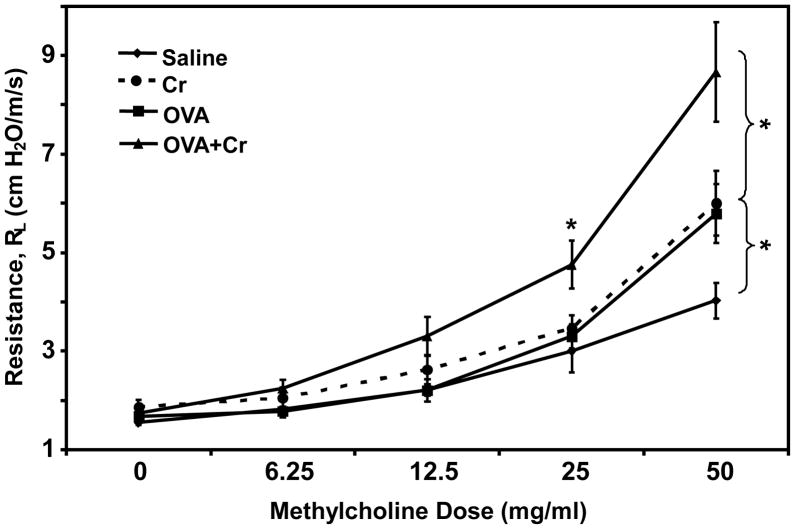
Figure 5.
Airway hyperresponsiveness to methylcholine. Mice were primed and challenged as indicated in Figure 1. On day 12, individual mice were anesthetized i.p. with ketamine/xylazine, a tracheostomy tube was inserted and then attached to a respirator. The animals were challenged with aerosolized PBS (baseline) followed by increasing doses of methylcholine ranging from 0–50 mg/ml. Maximum resistance (RL, cm H2O/m/s) was recorded during a 3-minute period following each challenge. Data are the mean ± SE from two independent experiments, with a total of 8–12 animals per group. Statistically significant differences among treatment groups was determined using a 1-Way ANOVA, * p < 0.05.