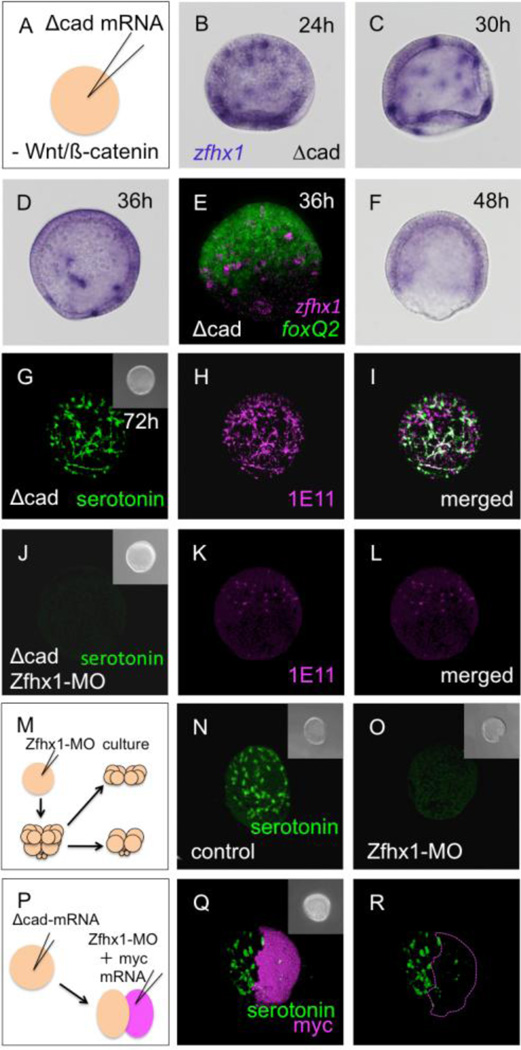
Figure 4.
Zfhx1/Z81 is required for the differentiation of serotonergic neurons. (A) Microinjection to inhibit canonical Wnt signaling. (B–F) The expression patterns of zfhx1/z81 in Δcad-injected embryos. (B) zfhx1/z81-positive neural precursors are scattered in the expanded 24-hpf embryo. (C) 30-hpf embryo. (D) 36-hpf embryo; the number of zfhx1/z81 cells decreased. (E) Double fluorescent in situ hybridization shows that zfhx1/z81 disappears from the central part of the animal plate. (F) zfhx1/z81 is down regulated in 48-hpf Δcad-injected embryos. The apparent staining in this embryo is background diffuse staining that is higher in the thickened ectoderm of these embryos. (G) Many serotonergic neurons differentiate in the expanded animal plate in Δcad-injected embryo. (H) All of serotonergic and non-serotonergic neurons in the animal plate are synaptotagminB (1E11 antigen)-positive. (I) Merged image of (G) and (H). (J) Δcad-injected Zfhx1/Z81 morphants have no serotonergic neurons at 72-hpf. (K) Serotonin-negative 1E11 neurons begin to differentiate in morphants. (L) Merged image of (J) and (K). (M) Method for creating animal caps from Zfhx1/Z81 morphants. (N) Serotonergic neurons differentiate in the glycerol-injected control animal cap. (O) No serotonergic neurons differentiate in the animal cap of Zfhx1/Z81 morphants. (P) Method to inject Zfhx1/Z81-MO and myc mRNA into one of two blastomeres derived from a Δcad-injected egg. (Q) Nearly all of the serotonergic neurons differentiate in the myc (i.e. Zfhx1/Z81-MO)-negative half of the embryo. (R) Only the outline of myc-positive, Zfhx1/Z81-deficient region of (Q) is shown. Insets are DIC images for each panel.