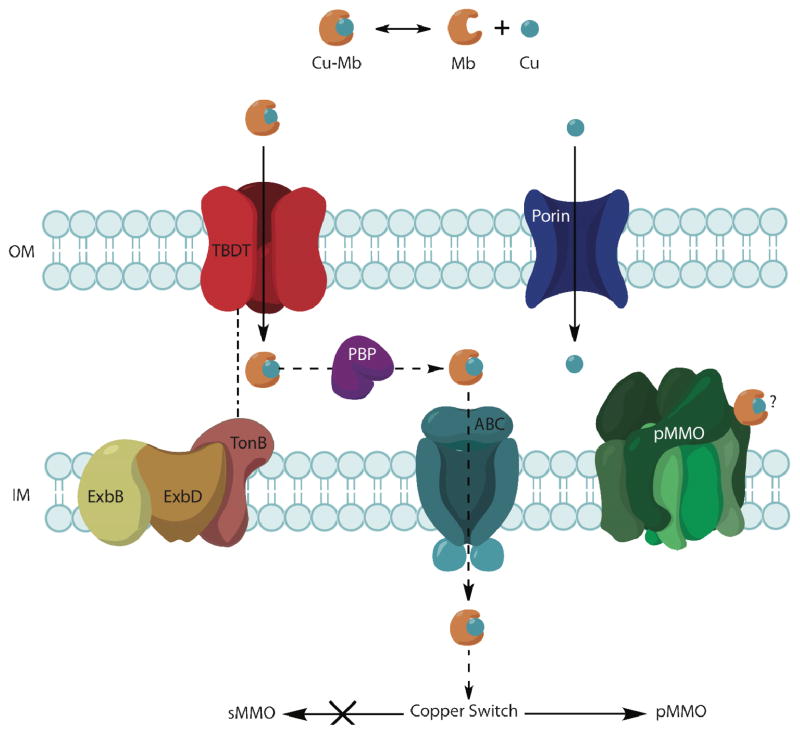
Figure 4.
Hypothesized uptake mechanisms for methanobactin and copper. Copper (Cu) is transported across the outer membrane (OM) by a passive transport process likely involving porins whereas Cu-Mb is transported via an active process potentially mediated by TonB-dependent transporters (TBDTs). The mechanism of translocation across the inner membrane (IM) is unknown, but by analogy to siderophores, could involve an ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter and a periplasmic binding protein (PBP). It remains unclear whether intact Cu-Mb interacts directly with pMMO or with proteins involved in the “copper switch.”