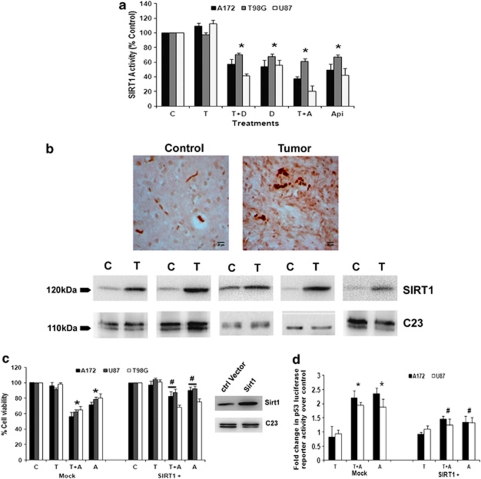
Figure 7.
CK2 inhibitor-mediated downregulation of SIRT1 activity regulates p53. (a) CK2-Is decrease SIRT1 activity in glioma cells both in the presence and absence of TNFα. Glioma cells were treated with TNFα in the presence or absence of DRB/Api and subsequently SIRT1 activity was determined. Values represent the means±S.E.M. from three independent experiments. (b) SIRT1 immuno-localization in glioma tumor samples as revealed by IHC and western blot analysis. Cryosections of glioma and adjacent normal tissues were immunostained for SIRT1 as described in Materials and Methods. Images were taken at 40 × magnification. Western blot analysis also demonstrated elevated SIRT1 levels in GBM tumor as compared with surrounding non-neoplastic tissue. The figure shows blots from five independent tumor samples with identical results. (c) CK2-I-mediated decrease in SIRT1 activity regulates glioma cell viability. The viability of glioma cells transfected with SIRT1 over-expression vector and treated with Apigenin or TNFα or both for 24 h, was determined by MTS assay. The graph represents percentage viable cells of control. Inset shows the overexpressed SIRT1 levels as determined by immunoblotting. (d) CK2-I-mediated increase in p53 transcriptional activity is abrogated upon SIRT1 over-expression. Glioma cells co-transfected with SIRT1 over-expression vector and p53 luciferase reporter constructs were treated with Apigenin or TNFα or both and reporter assay was performed to determine p53 transcriptional activity. The graph represents fold change in p53 luciferase reporter activity over control. Values in (a, c and d) represent the means±S.E.M. from three independent experiments. *Denotes significant change from control (P<0.05), #denotes significant decrease from mock-transfected CK2-I-treated cells (P<0.05)