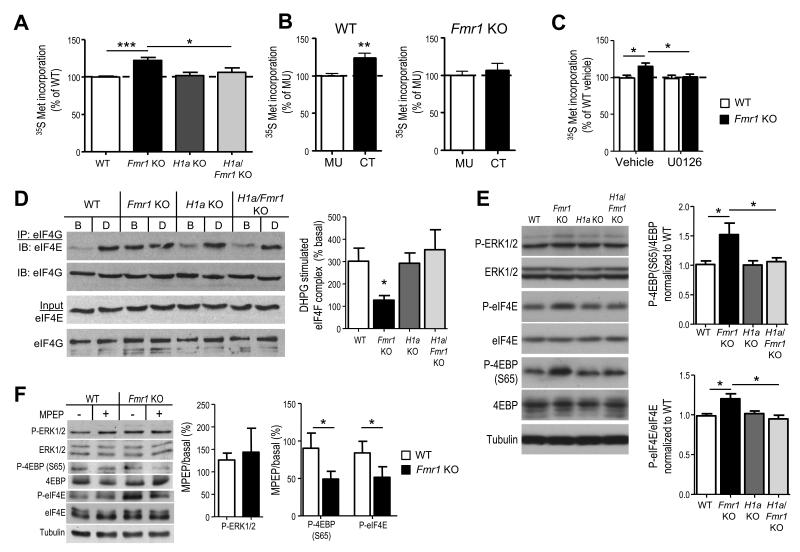
Figure 3. Altered mGluR5-Homer scaffolds in Fmr1 KO mice mediate enhanced basal translation rates and initiation complex formation.
A. Acute hippocampal slices from Fmr1 KO mice display elevated protein synthesis rate in comparison to WT littermates as measured by incorporation of 35S Met/Cys into total protein (n = 14 slices from 7 mice/genotype). Elevated protein synthesis rates in Fmr1 KO slices are reversed by H1a deletion (H1a/Fmr1 KO; n = 7 slices/ 4 mice), whereas H1a KO alone (n = 8 slices/4 mice) has no effect. B. Pretreatment of WT hippocampal slices with mGluR5CT (CT; 5 μM; 5 hours; n = 16 slices/4 mice) enhanced 35S Met/Cys incorporation in comparison to control (mGluR5MU; MU; n = 16 slices/ 4 mice) peptide. In contrast, pretreatment of Fmr1 KO hippocampal slices (n = 15 slices/ 4 mice) with CT peptide had no effect. C. Preincubation of WT or Fmr1 KO slices with an inhibitor of the upstream kinase of ERK (MAP/ERK kinase; MEK) U0126 (20 μM; 30 min) prior to 35S Met/Cys incorporation (n = 12 slices/ 6 mice per condition) equalizes protein synthesis rates. D1. Representative Western blots of eIF4E that co-immunoprecipitated with eIF4G from hippocampal slices reveal that DHPG (D) induces an increase in eIF4E association with eIF4G, forming the translation initiation (eIF4F) complex, in WT but not in Fmr1 KO littermates despite an elevated level of eIF4F complex under basal (B) conditions. H1adeletion alone has no effect on eIF4E/4G levels under basal or DHPG stimulated conditions, whereas, H1a deletion on the Fmr1 KO background reverses the enhanced eIF4F complex levels and restores DHPG induced eIF4F complex formation. D2. Quantified group data of the levels of eIF4E that coimmunoprecipitated with eIF4G (eIF4E/4G) in DHPG treated samples (normalized to the levels of eIF4E/4G in basal, or untreated slices). n = 3 mice per genotype. E1. Representative Western blots of phospho- and total ERK and translation initiation factors that are regulated by ERK, (phospho- and total eIF4E and 4EBP) from cortical homogenates in each of four genotypes. E2. Quantified group data reveals elevated P-4EBP and P-eIF4E in Fmr1 KO brains as compared to WT, which is rescued by H1a deletion. P-ERK levels were not different across any genotype (n = 4-6 mice per genotype). F1. Representative Western blots from acute hippocampal slices prepared from WT and Fmr1 KO mice treated with MPEP (10 μM) or vehicle (H2O). F2. Quantified group data of the level of phosphoproteins in MPEP treated slices expressed as a percent of basal (untreated) slices reveals a genotypic difference in P-4EBP (S65) and P-eIF4E, but not P-ERK (n = 2 slices/mouse; 4-8 mice/condition). *p< 0.05; **p< 0.01; ***p<0.001. Full length western blots for this figure are shown in Supplementary Fig. 9.