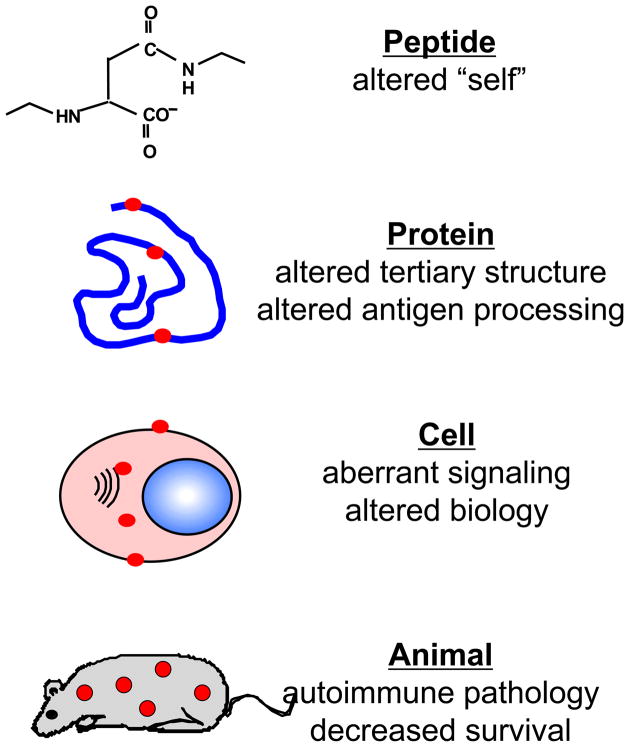
Figure 1.
The multiple effects of posttranslational modifications. The effects of posttranslational modifications can be seen on multiple levels. Posttranslationally modified peptides become sources of altered self, and when in the context of proteins, can affect the tertiary structure of a protein and how it is processing by antigen processing cells. When significant amounts of certain posttranslational modifications accumulate in cells, they also have the potential to alter how the cell functions (i.e., proliferation rates, cell signaling). Finally, the culmination of all of these individual effects is the onset of autoimmune pathology in whole organisms and ultimately decreased survival.