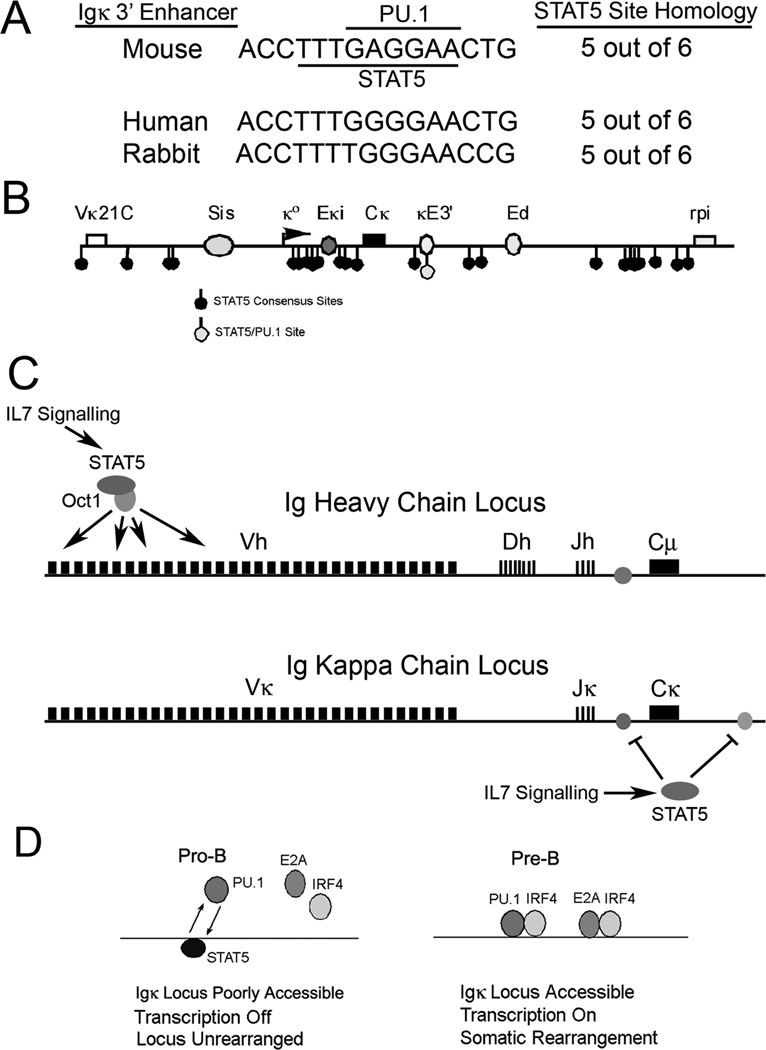
FIGURE 7. Model for STAT5 inhibition of Igκ locus accessibility.
(A) The overlapping PU.1 and STAT5 binding sites are conserved in κE3’ enhancer sequences from mouse, human and rabbit. (B) Location of putative STAT5 sites within the Igκ locus. Numerous STAT5 consensus sequences are observed within the Igκ locus, but only a single site within the κE3’ enhancer overlaps with a PU.1 binding site. Locations of Vκ21C and rpi genes, and Sis, Eκi, κE3’, and Ed enhancers are indicated. (C) IL7 signaling activates IgH distal V gene rearrangement through STAT5 while simultaneously reducing Igκ locus accessibility through inhibition of Igκ intron and κE3’ enhancers. (D) Model for STAT5 function at the κE3’ enhancer during the pro-B to pre-B cell transition. In pro-B cells IL7 signaling activates STAT5 which competes with PU.1 for binding to the enhancer leading to low IRF4 and E2A occupancy and low κE3’ enhancer activity. In pre-B cells, loss of IL7 signaling and increased IRF4 expression enables PU.1, IRF4 and E2A to bind to the κE3’ enhancer leading to increased activity, and stimulation of Igκ rearrangement.