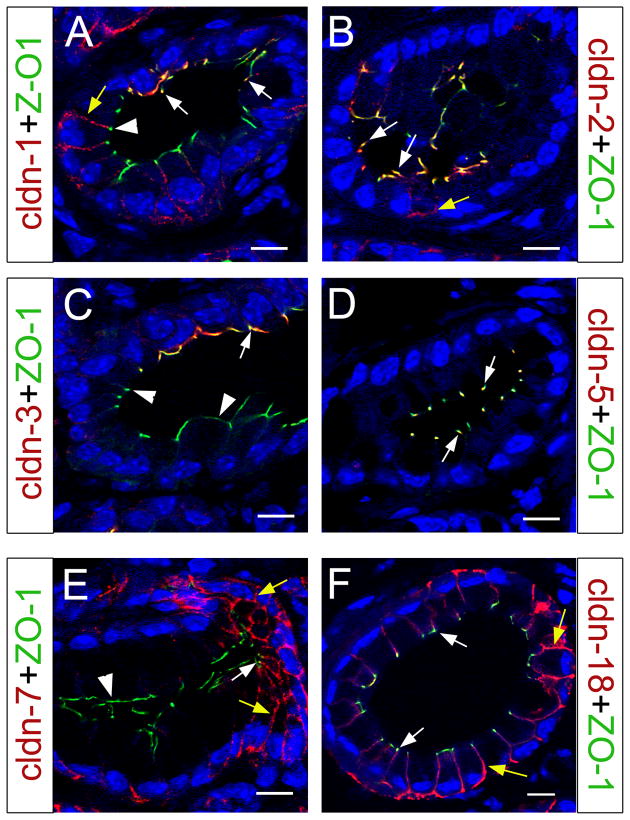
Figure 8. Subcellular localization of claudin proteins in PanIN-1A lesions.
(A) PanIN-1A lesion showing claudin 1 co-localization with ZO-1 in TJs of cells with normal morphology (arrows). In more transformed cells with abundant cytoplasm claudin 1 does not co-express with ZO-1 (arrowhead) but appears distributed to the lateral membrane (yellow arrow). (B) Claudin 2 mainly localizes to TJs (white arrows) in PanIN-1A epithelia, although a few cells also exhibit lateral distribution of this protein (yellow arrow). (C) Claudin 3 proteins specifically localize to TJs (white arrow) of normal appearing PanIN-1A epithelial cells (arrow; arrowheads indicate portions of the transformed epithelium devoid of claudin 3 expression). (D) Claudin 5 is detected in all TJs in the PanIN-1A epithelium (white arrows). (E) Claudin 7 proteins localize to both TJs (white arrow) and the lateral membrane (yellow arrows) in portions of the PanIN-1A epithelium, whereas is absent in TJs of cells with abundant cytoplasm (arrowhead). (F) Claudin 18 proteins extensively localize throughout the PanIN-1A epithelium, both in TJs (white arrows) and in the lateral membrane (yellow arrows). All images were taken with a confocal microscope, and cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 10 μm.