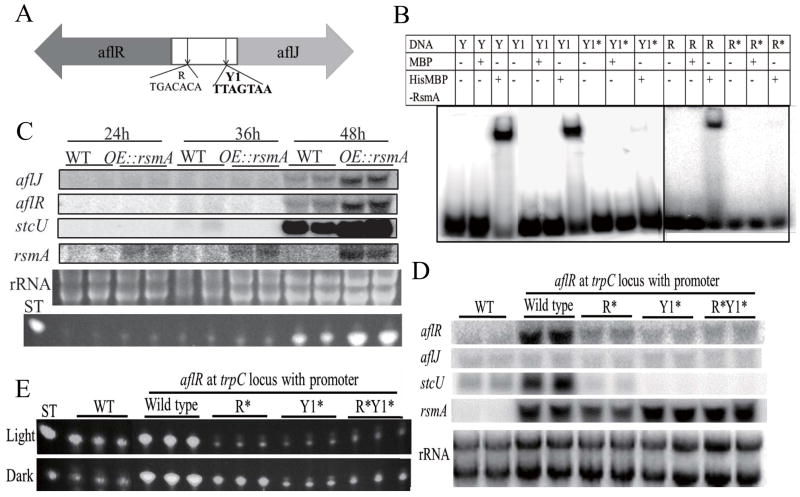
Figure 4. RsmA activates aflR and aflJ expression by specific DNA-binding in the aflR/aflJ divergent promoter.
Panel A RsmA binding sites in the promoter region of aflR/aflJ. Y1: yeast Yap 1 site, R: RsmA site.
Panel B. Specific binding of RsmA to the aflR/aflJ promoter. The purified maltose binding protein (MBP)-tagged RsmA or MBP alone was incubated with the following 32P-labeled sequences: Yap 1 binding site (Y: TTACTAA), Yap 1 binding site in the promoter region of aflR/aflJ (Y1: TTAGTAA), a mutation in this Y1 site (Y1* = TAAGTTA) and RsmA site (R = TGACACA and R*=AAACAGG). *=mutated sequences.
Panel C. rsmA overexpression results in increased aflR, aflJ and stcU expression. RNA was extracted after 24, 36 and 48 h of growth in liquid shake cultures. ST production from the same samples, as analyzed by TLC, is shown below rRNA. Ethidium bromide-stained rRNA is shown as a loading control.
Panel D. RsmA binding sites are required for aflR expression in vivo. aflR, aflJ, rsmA and stcU expression in five strains: WT (RDIT9.32), aflR with WT promoter at trpC locus (TWY18.14), aflR and promoter with R* mutation at trpC locus (TWY19.15), aflR and promoter with Y1* mutation at trpC locus (TWY20.4) and aflR and promoter with R* and Y1* mutations at trpC locus (TWY21.20). RNA was extracted after 48 h of growth in liquid shake cultures. Ethidium bromide-stained rRNA is shown as a loading control.
Panel E. ST production from strains shown in Panel D.