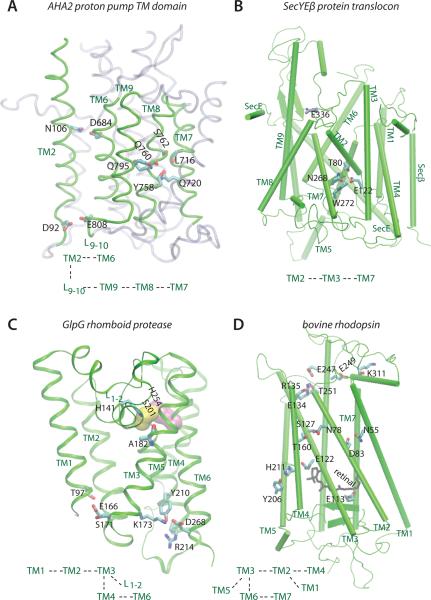
Figure 2.
Examples of networks of H bonds that interconnect TM helices of different classes of membrane proteins. Only selected H-binding amino acids sidechains are depicted explicitly. Each panel is accompanied by a schematic representation of the inter-helical connections mediated by H bonds. (A) The AHA2 P-type plasma membrane proton pump (PDB ID: 3B8C). For simplicity, TM helices that do not participate in the H bonds depicted explicitly are shown as transparent gray ribbons. (B) The central cluster in the SecYEβ protein translocon (PDB ID: 1RHZ). E122 of TM3 mediates a cluster of H bonds that involve amino acids of the gate helices TM2 and TM7; E122 is highly conserved as Glu in archaea and eukarya, and present mostly as Gln in bacteria [11]. (C) The rhomboid intramembrane protease (PDB ID: 2IRV). The catalytic groups Ser201 and His254 are shown as yellow and purple surfaces, respectively. (D) Bovine rhodopsin with the retinal cofactor shown as black bonds (PDB ID: 1U19). E134 and R135 are part of the conserved E(D)RY motif. At 3.9 Å the distance between the E122 and H211 sidechains is somewhat long for an H bond, but in a flexible protein environment that distance could easily sample H-bonding values. The molecular graphics images in panels A–D were prepared using the VMD software [52] based on published crystal structures [4, 9, 19, 53]. The simulations of SecYEβ and GlpG were performed using the CHARMM [54] force field parameters for the protein [55] and lipid [56] atoms, and the TIP3P water model [57]. The length of the bonds involving H atoms are constrained using the SHAKE algorithm [58], the short-range interactions are cut-off at 12 Å using a switching function between 8Å and 12Å, and the Coulomb interactions are computed using the smooth particle mesh Ewald summation [59, 60]. Langevin dynamics were used to maintain the temperature constant at 300K (POPC lipids) or 310K (POPE lipids), and a Nosé-Hoover thermostat [61, 62] for keeping the pressure at 1bar. After an initial equilibration with weak harmonic constraints (2kcal mol−1 to 5 kcal mol−1) and an integration step of 1fs, we switched off all harmonic constraints and used the reversible multiple time-step algorithm [63, 64] with integration time-steps of 1fs for the bonded-forces, 2fs for the short-range non-bonded forces, and 4fs for the long-range electrostatic forces. MD simulations of GlpG were based on the crystal structure of Ben Shem et al [19]; the simulation systems comprised ~160,000 atoms (~500 lipid molecules, solvent water, and ions for charge neutrality). In the MD simulation of the SecYEG translocon we used the crystal structure of Van den Berg et al. [9] for the protein atoms, and a patch of 475 POPC lipids (217,820 atoms including solvent water and ions for charge neutrality).