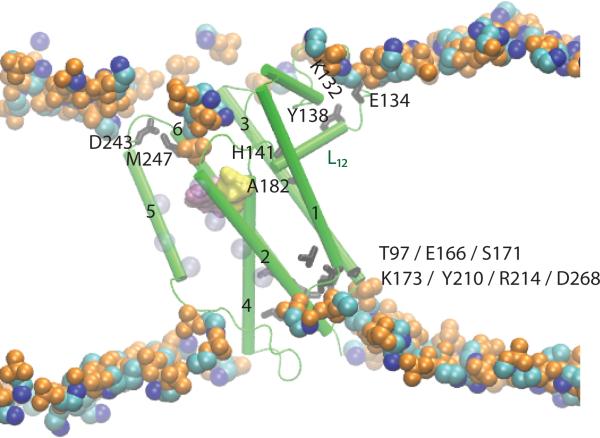
Figure 5.
Lipid and intra-protein H bond coupling in GlpG. The active site groups S201 and H254 are shown as yellow and purple surfaces, respectively. Loop L12 H bonds to the POPE lipid membrane via E134, and to the protein via the L12-H141:TM3-A182 H bond. TM3 further connects via H bonding to TM1, TM2, TM4, and TM6 (see also Figure 2C). TM2 is connected to the gate helix TM5 via hydrophobic interactions; these interactions are illustrated schematically by the transparent blue van der Waals spheres on TM2 and TM5, which represent the Cα atoms of amino acids L161, W157, and F153 TM2, and L229, F232, W236 on TM5. The sidechain:backbone interaction between D243 and M247 is significantly more stable in POPE than POPC lipids [22]. In a POPC lipid bilayer the H bond between the Y138 sidechain and the K132 backbone is broken as water molecules penetrate deeper into the lipid membrane. Figure 5 is modified from Bondar et al. [22].