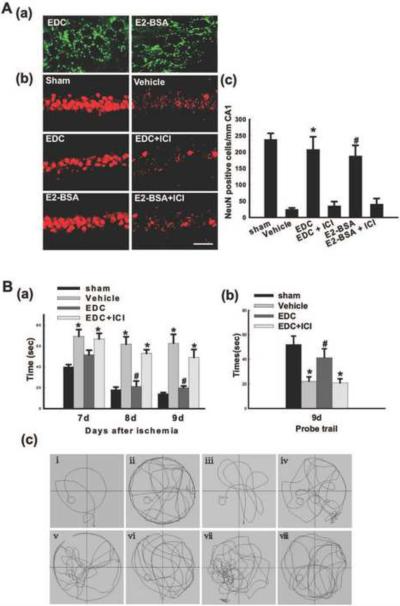
Figure 4.
(A-a) Extranuclear localization of EDC and E2-BSA in neurons in hippocampal CA1 region of rats. FITC-tagged EDC and E2-BSA were injected into the lateral ventricles. 1h later, the rats underwent transcardial perfusion, and their brains were cut into 25mm coronal brain sections with a cryostat. Confocal analysis showed that EDC and E2-BSA entered neurons in the hippocampal CA1 region but were incapable of penetrating into the nucleus. (A–b, c) EDC and E2-BSA2 protect neurons of the hippocampus CA1 region from injury induced by GCI. NeuN immunostaining of representative hippocampus sections from sham, vehicle, EDC, EDC+ICI, E2-BSA and E2-BSA+ICI-treated female ovariectomized rats subjected to 10min GCI followed by 7d reperfusion. Global ischemia induced significant neuronal cell loss in the CA1 pyramidal cell layer. EDC or E2-BSA treatment afforded nearly complete protection from global cerebral ischemia-induced neuronal cell loss. ICI182,780 (ICI) abrogated the neuroprotection induced by EDC or E2-BSA. NeuN-positive neurons per 1 mm length of CA1 region were counted as surviving neurons. F (5, 30) = 105, *P < 0.001 vs. vehicle and EDC+ICI groups; F (5, 30) = 105, #P < 0.001 vs. vehicle and E2-BSA+ICI groups. Magnification, 40×; Scale bar, 50μm. (B) Effects of EDC on spatial learning and memory ability in the Morris water maze. (a) Latency to find the submerged platform. F (11, 48) = 77, *P < 0.001 vs. sham; F (11, 48) = 77, #P < 0.001 vs. Vehicle and EDC+ICI. (b) Time spent in the quadrant, which initially contains the platform. F (3, 16) = 37, *P < 0.001 vs. sham; F (3, 16) = 37, #P < 0.01 vs. Vehicle and EDC+ICI. (c) Representative sample paths from the maze trials (i–iv) and the probe trials (v–viii) at 9 days after reperfusion. (i, v: sham; ii, vi: vehicle; iii, vii: EDC; iv, viii: EDC+ICI). R: reperfusion. ICI: ICI182,780. Reprinted, with permission, from PLoSOne [194].