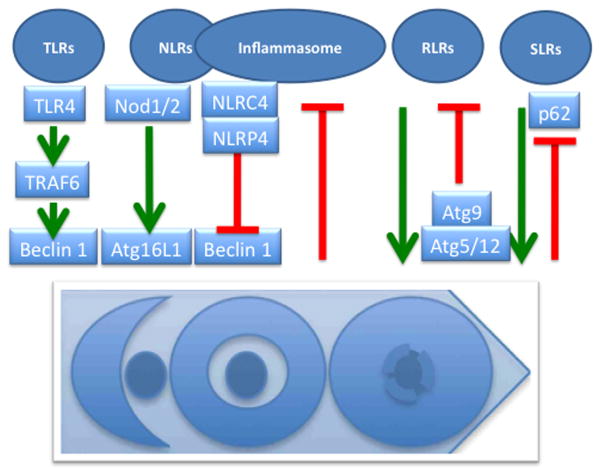
Fig. 3. Pattern recognition receptors, inflammasomes, and autophagy.
NLRs, Nod-like receptors. RLRs, RIG-I-like receptors. SLRs, Sequestome 1/p62-like receptors. TLRs, Toll-like receptors. All are collectively referred to as pattern recognition receptors (PRRs). Positive regulation of autophagy by PRRs can occur via TRAF6 downstream of TLR4 (TRAF6 ubiquitinates Beclin 1 and releases it from inhibitory complexes with Bcl-2), or via direct interactions with Atg factors (e.g. Nod1/2-Atg16L1). Negative regulation of inflammasome by autophagy is presently ascribed to autophagic prevention of formation of the endogenous sources of inflammasome agonists (e.g. reactive oxygen species or DNA released from unkempt mitochondria). Atg5-Atg12 can negatively regulate RLR signaling by binding and interfering with RLR signaling complex formation (e.g. Atg5-Atg12 conjugate binding to VISA/IPS-1/Cardif/MAVS located on mitochondria). SLRs as autophagic adaptors play a positive role in autophagic elimination, whereas autophagy degrades (and thus downregulates) SLRs in the process of autophagy.