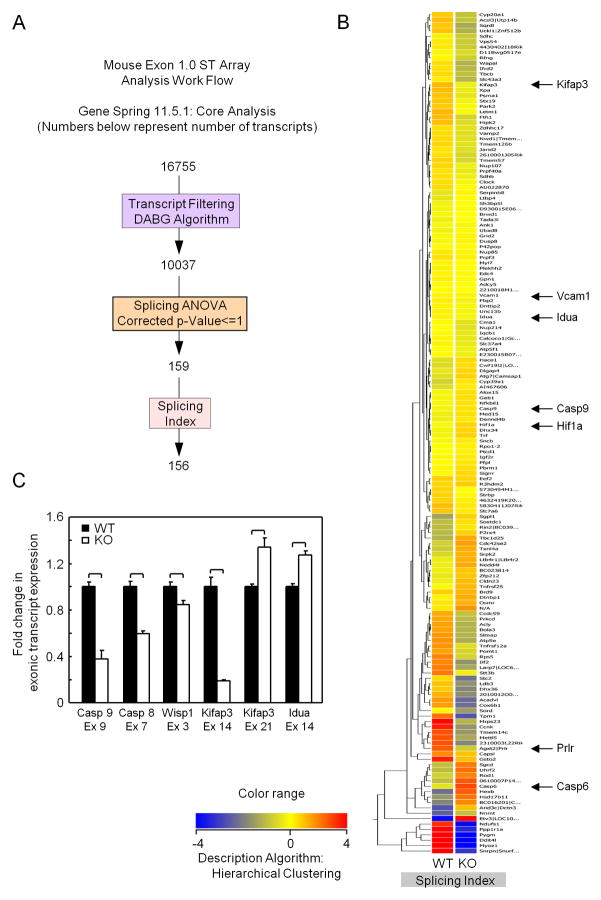
Figure 3. Genome-wide splicing array demonstrates endogenous c-jun governs alternative splicing.
Exon inclusion or exclusion (resulting from altered mRNA splicing) were compared in exon arrays using LCM RNA from mammary epithelium of Cre+/c-junf/f (c-jun−/−) versus Cre+/c-junw/w (c-jun+/+). (A) Schematic representation of the alternative splicing analysis on Affymetrix Exon Arrays using Gene spring. (B) Primary Heat Map depicting the splicing index of 81 differentially spliced genes among c-jun WT and KO. Blue lines indicate expression of probe set in WT c-jun (c-jun+/+) and red lines indicates in KO (c-jun−/−) mammary epithelial cell RNA. (C) Graphical representation of exonic inclusion or exclusion of six biologically relevant genes involved in apoptosis showing alternatively spliced exons. Mean transcript exclusion or inclusion data is represented for each of the probe set IDs with 3 samples for each sample type from c-jun+/+ and c-jun−/− animals. *p ≤ 0.05, Error Bars = Standard Deviation.