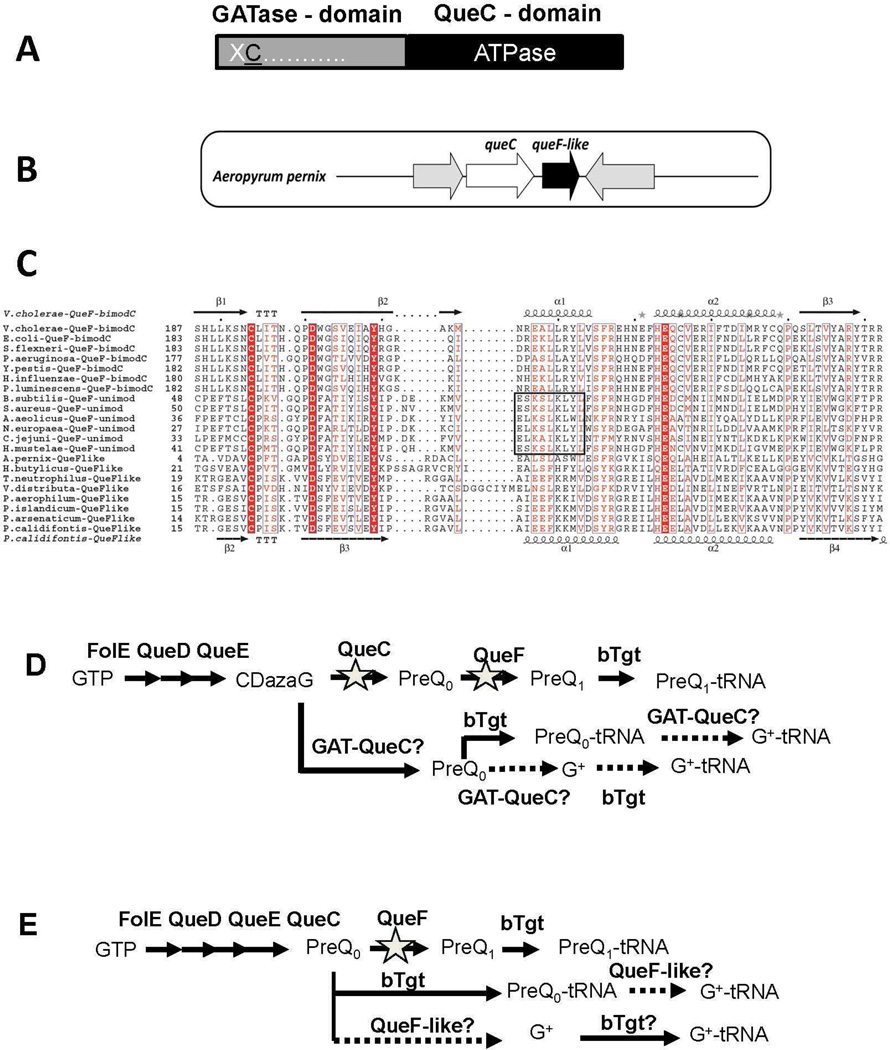
Figure 2. Analysis of the GAT-QueC and QueF-like protein families.
A) Two domain organization of GAT-QueC enzymes; B) Physical clustering of queF-like with queC in A. pernix; C) Structure-based multisequence alignment of QueF and QueF-like proteins. Invariant residues of the substrate binding pocket are highlighted in red. The QueF motif in unimodular QueF is boxed. Secondary structure elements from the V. cholerae QueF crystal structure and from the P. calidifontis QueF-like homology model are shown above and below the sequences, respectively; D) Design of E. coli test strain; in the E. coli K12 MG1655 strain, the queF and queC were deleted, and the resulted deletion strain was transformed with an expression plasmid containing GAT-queC from S. solfataricus (SSO0016) cloned behind a PBAD promoter. E) Design of the E. coli test strain; queF was deleted in E. coli K12 MG1655, and the resulting deletion strain was transformed with an expression plasmid containing queF-like from P. calidifontis (Pcal_0221) cloned behind a PBAD promoter.